High-quality military clothing is the key to high combat effectiveness of the army. The modern Russian military uniform meets all the requirements: it is comfortable, reliable and functional. A new military uniform was released in our country in 2019, and now every soldier of the armed forces is equipped with it.
Military uniforms are divided into three main types:
- Front - used during ceremonial events (at parades, during military holidays, at ceremonies for receiving military awards, etc.);
- Field - used during hostilities, service, providing assistance to civilians during natural disasters, etc .;
- Office - used in cases not related to the first two categories.
Global reform of the form of the Russian army
The modern history of Russia has several failed attempts change uniforms of military personnel. While in our country a lot of money was spent on unsuccessful experiments, in the US Army, military clothing became more comfortable, its performance characteristics increased, and innovative materials were used in the production of clothing.
The modern military uniform began its journey in 2007, when Anatoly Serdyukov held the post of Minister of Defense. It was then that a large-scale sketch competition was organized, in which thousands of designers from all over the country took part. The Ministry of Defense awarded the victory to the famous designer Valentin Yudashkin.
For the next two years, specialists were engaged in the development of final versions of a new army uniform, intended for further equipment of the Russian army. The result was a set of clothes, in many ways similar to American uniforms. The developers did not agree with this opinion, although many factors spoke precisely in favor of this comparison.
Winter military uniforms caused particular dissatisfaction. She did not protect the soldiers from the cold. For this reason, the Ministry of Defense received many complaints every day about the inadequate quality of the winter kit. This led to an outbreak of colds among the military. There were also complaints about the appearance of the uniform: some stylistic decisions were copied from kits from other countries. The stumbling block was the quality of the fabric and threads: new military clothing quickly fell into disrepair.
Negative reviews, dissatisfaction with soldiers and army specialists made the Ministry of Defense think about changing the equipment. The decision to take American clothes as a basis was erroneous, such suits did not fit the conditions of our country. A new set of military uniforms, developed subsequently, consisted of 19 parts. The approximate cost of one set is 35 thousand rubles. The parade version did not suffer any special changes, since it is the field uniform that is of particular importance.
New field military uniform of the RF Armed Forces
The first change that caught your eye was the change in the location of the shoulder straps on the uniform. In 2010, the "NATO" version was proposed, shoulder straps in it were located on the "belly". Many servicemen did not like this, as they were "used to seeing epaulettes on their shoulders." Chevrons on the uniform are located on both sleeves. The addition was the appearance of fitted overcoats, quickly fastened elements of clothing with Velcro. For the first time in history, Russian officers received warm sweaters. It was not possible to completely replace footcloths and boots.
Valentin Yudashkin was blamed for the failed project of a new military suit. In 2012, he spoke to reporters and stated that the clothes adopted for use are very different from his version. In particular, in order to reduce the cost, materials were replaced with lower quality ones. The journalists came to the conclusion that only appearance.
The new generation military uniform was developed based on the feedback of thousands of soldiers from all over the country. The shape of the sun has become multi-layered. This allows each soldier to independently choose the necessary elements of clothing, guided by the goals and objectives set for him, as well as weather conditions.
The modified VKPO kit includes a basic suit, several types of jackets, boots for different seasons and much more, including a balaclava, a synthetic belt and quality socks. Tailoring of military uniforms is carried out from a blended fabric, which includes 65% cotton and 35% polymer materials.
Russian military clothing of the new model was in every soldier at the end of 2019, as previously planned by the Ministry of Defense. The change of equipment took place in three stages. In 2013, 100,000 new kits were issued, in 2014 - 400,000 and in 2019 - 500,000. For 3 years, a million military personnel were provided.
The complete rejection of footcloths deserves special attention. Modern military uniforms include 12 pairs of socks for one soldier, which he wears for a year. In the near future, it is planned to increase the number of pairs per military man to 24 pieces.
VKPO sets for wearing at different atmospheric temperatures
The military uniform of the new sample is presented in two sets:
- Basic uniform for wearing at temperatures above +15 degrees Celsius;
- Multi-layer system for wearing at temperatures from +15 to -40 degrees Celsius.
AT winter period soldiers wear lightweight or fleece underwear sets. They are selected depending on the air temperature. In particularly cold areas, both sets of underwear can be worn one on top of the other.
For equipment in the summer season, trousers, a jacket, a beret and boots are used. The surface of the garment is carefully treated with an innovative solution that repels moisture. It allows clothes to stay dry in the rain for up to two hours. For protection against mechanical influences, military clothing is equipped with reinforcing elements. Such kits are used in parts with a high degree of load.
The rules for wearing military uniforms allow the use of a fleece jacket in the autumn season: excellent thermal insulation is provided by the pile with which it is covered on both sides. From strong winds, a windbreaker jacket is worn with trousers of the fifth layer.
For the autumn period, a demi-season military suit is intended. The material from which it is made provides reliable protection from the wind, a good degree of vapor permeability and dries quickly after getting wet. During heavy rains, it is permissible to use a wind and water protection kit. The membrane and reliable sizing of the layers provide reliable protection against moisture.
In winter, a warm jacket and vest are worn, which protect against moisture and wind. In spite of a high degree protection against frost, they are light and practical. For very low temperatures, a warm hat and balaclava are provided.
Modern full dress military uniform of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation
The design basis of the dress uniform has not changed for many years, as it still meets modern requirements and at the same time pays tribute to history. Only a few elements have been replaced in last years due to their obsolescence. Dress uniforms are worn at parades, holidays, when receiving military awards, etc.
In the Russian army, there are three approaches to the formation of such a set of uniforms:
- Traditional. Clothing sets include elements created back in the 19th century. good example the ceremonial set of the Presidential Regiment of the Russian Federation serves - their costumes are identical to the uniform of the Imperial Guard, adopted in 1907;
- Modern. The cut of the dress uniform corresponds to the daily set, the same colors can be used. For example, in the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, the color of the ceremonial tunic matches the everyday one. Everyday elements are complemented by ceremonial elements;
- Universal. The color of the ceremonial suit may be the same as the everyday one, but the colors of the ceremonial elements must be different without fail.
The parade uniform in strict order must comply with the following standards:
- The stylist of the military uniform of the military personnel of the Russian Army must be observed;
- A military dress for parade purposes should be strict and elegant;
- In production, only high-quality materials should be used.
Changes to the design of the dress uniform are rarely made, its main style is determined by history. Various optional items may change each year. A change in the materials used in production is only permissible if it improves the quality and performance of the suit.
Noteworthy is the general's ceremonial attire. It is also similar to a casual suit, but has a different color scheme. The color of the dress uniform is gray, worn with bluish trousers and black boots. There are patches on the collar and cuffs.
Everyday uniform of military personnel
The color of the daily uniform depends on the rank and affiliation. Military clothing of the Russian army of everyday type for generals and officers is olive in color, in the Air Force - blue. Caps match the color of the outfit. The color scheme was based on the 1988 pattern. The decorative elements on the caps are painted gold. Men's winter clothes have not changed since the last reform.
Girls in military uniform can now feel comfortable. Dresses and skirts comfortably fit the body, emphasizing feminine beauty. Women's military clothing - olive or blue. AT winter time year, a shortened, fitted coat is used. Female sergeants and enlisted men wear an olive daily uniform. In the warm season, there should be a cap on the head, in winter - an astrakhan beret introduced by the latest reform.
Sergeants, soldiers and cadets of everyday uniforms are deprived due to uselessness. Alternatively, they are encouraged to wear winter or summer field gear.
The military uniform of this type in the winter period of the year provides for a gray coat for military personnel (blue for the Air Force and Airborne Forces). A demi-season jacket is provided for the autumn period of blue color, for rains in summer time years - an elongated raincoat that does not let moisture through. Black coloring for additional items of clothing (belt, boots and socks).
Modern office uniform of the Russian army
Such a set of clothes is a kind of everyday wear, used by generals, officers and employees of the Ministry of Defense of certain ranks. A military suit of this kind resembles the everyday clothes of the Ministry of Emergencies. The kit includes:
- Soft cap. All military units Green colour, units of the Airborne Forces were left with a blue beret;
- Cap-colored shirt with long or short sleeves (the choice depends on the weather). Velcro straps can be attached to the shoulders, a tie is not applicable;
- White T-shirt (worn under the shirt);
- Cap-colored trousers and straight-cut shirts.
In the cold season with an office uniform, the use of a warm jacket is acceptable. It is possible to attach an additional hood. The cap can be replaced with a warm hat with earflaps. Velcro straps are attached to the shoulders of the costume.
Each year, the office uniform undergoes minor changes. These include the introduction and abolition of various costume sewing, changing the shape of insignia, etc. It is forbidden to use an office suit as a field suit. Care and rules for wearing military uniforms
The rules for wearing military uniforms are regulated by order 1500 - the suit must always be clean. To keep it that way, you need to know about some of the intricacies of caring for it. Improper washing or drying can spoil the appearance, which will lead to official troubles. Before cleaning clothes, read the information on the label.
Woolen clothing is recommended to be washed by hand in warm water. If this is not possible, then you can use the washing machine, but the washing mode should be the most gentle. Military clothing sizes can become smaller if washed with hot water. Wringing wool products is prohibited.
Everyday military equipment is less whimsical to care for. It can be washed in the washing machine in any mode with any detergent. In addition, a casual suit is able to withstand water of any temperature.
It is not recommended to clean a beautiful dress uniform at home. This process is best entrusted to professionals in the dry cleaning service.
The new Russian military clothing, put into service in 2019, surpasses the previous generation in all respects. This became possible after the refusal to copy the American design, unsuitable for the climatic conditions of our country. The military uniform of the Russian Federation is considered one of the best in the world.
If you have any questions - leave them in the comments below the article. We or our visitors will be happy to answer them.
Tank helmet model 1936 photo Headphone flaps moved back from the cylindrical vertical columns. The rollers were stuffed with hair (technical cotton wool was also used to fill the avisent rolls). Radio equipment was housed in enlarged sinuses and pockets with adjustable flaps. The backplate could be bent, the top was pulled together by a transverse strap. The sides of the helmet cap, issued before the war, had ventilation holes with blocks. From the end of 1942, a significant part of tank helmets were equipped with aircraft-type radio equipment - oval blackened metal cups for telephones, a laryngphone and connecting cords with connectors. tank helmet 1936, materials changed. Dark blue moleskin tanker overalls with patch pockets and a detachable back flap, the belt of which, which had a sliding buckle, was usually covered by a waist belt.
Uniform of the Red Army 1918-1945 (143 photos)
But old photos show that they are often preserved until the introduction of shoulder straps in 1943. The soldier wears windings - which were of various colors, made from all kinds of worn out uniforms and boots.
Junior sergeant, infantry elements of equipment 1941, corps commissar Several million pairs of boots were supplied by the USA under Lend-Lease of the USSR. Armed with a Mosin rifle or a three-ruler model 1938, leather pouches for ammunition, a canvas bag for two RGD-33 hand grenades and a gas mask.
At the beginning of the war in the Red Army 13 cavalry divisions, although they have been significantly reduced due to the course towards the mechanization of the army since the late 1930s. In August 1941, the size of the cavalry division was reduced to 3,000 people - in fact, brigades - but the number of divisions was increased, reaching 82 by the end of 1941.
Cavalryman, Red Army 1941
- It is described in detail here: The military uniform of the Wehrmacht soldiers Eastern Front.
- Here: German military uniform of the second world war.
- Here: Military uniform of the Soviet Red Army. photo. Red Army military equipment photo equipment description 1.Officer's belt sample 1932 and 1943 2.Officer's belt sample 1935. 3.Soldier's leather belt 4.Junior command belt 5.Soldier's canvas belt 6.Helmet model 1916 7.Helmet model l936g. 8. Helmet of civil defense l938g 9.
Helmet model 40 years M 1940 10. glasses 11. types of commander's tablets On February 1, the order of the People's Commissar of Defense No. 005, which provided for the unification of the uniform and its adaptability to wartime conditions. The February order of 1941 was stamped "top secret".
This is to the fact that the USSR did not know about the impending invasion, it knew and was actively preparing.
to home
Attention
And the field one was leather, with a two-pronged frame buckle, curly stitching, shoulder straps that overlapped on the back or with the help of a diamond-shaped ring. Military and combat equipment of the Soviet Red Army 1.
Holster for revolver Nagant, 1941, 2.3. Leather holster for revolver Nagan4. Box arr. 1930 for ammunition for the machine gun "Maxim"5.
Important
Goggles for tankers, motorcyclists, submariners and torpedo pilots arr. 19366. Flight goggles7. Bayonet scabbard8. Leather holster for TK-269 pistol.
Leather holster arr. 1932 for TT pistol10.Ax case11.Knife for opening ammo boxes12.Sunglasses for skiers13.Holster for signal pistol SPSh14.Small sapper shovels with covers15.Gun accessory (rifle, submachine gun)16.Spare cartridge bag17.Waterproof grocery bag arr.
It is naive to think that the role of the cavalry was small, here is an excerpt from Shederovich’s dialogue “and how did we meet the fur of the Wehrmacht corps, the cavalry of Dovator”, and he does not know that in the most difficult days of the beginning of the war, only the cavalry could react mobilely to the breakthroughs of the German wedges, and she threw herself under these wedges, often after a march of 200-500 km, do you think at least one tank unit will be able to march at least 300 km? There was an attempt at the beginning of the war to hit the flank of the German wedge, with a tank formation after the march, and so 80% of the tanks simply did not reach. In the instruction of 1933, the cavalry was ordered to lead fighting dismounting. The heyday of the cavalry was in 1942, during the campaign in the south: although tactically outdated, the cavalry troops made a huge contribution to the local conditions of the front, and fulfilled the role of mobile troops, while the Red Army built up tank troops.
Summer uniforms of the Red Army for the period 1940-1943:
Introduced into the Red Army on January 1, 1932. A camouflage suit, in cut, which was a wide loose blouse worn over the head. A hood was sewn to the neck, which was tightened with laces according to the shape of the head or along the lower edge of the steel helmet, leaving only a narrow strip of the face open. White hoodies worn over overcoats and short fur coats were used. Steel helmets were whitewashed - with chalk or lime. a shooter in winter camouflage of 1939-40 and a shooter in winter marching uniform of 1939-41 Command and command personnel wore leather belts with a stamped frame buckle, inside of which was placed a five-pointed star with a hammer and sickle in a round medallion.
The belt fastened on a brass peg to the left of the buckle, had sewn-in brass half-rings for the shoulder strap and figured stitching; It was also used as everyday lightweight equipment.
Oh msbro!
The sleeves at the cuff sewing have two folds. At the back of the sleeves over the elbow seam there are overhead elbow pads. On both sides of the collar, edged buttonholes are sewn in the color of the cloth assigned to the military branch.
Buttonholes have the form of a parallelogram with a finished length of 8 cm and a width of 3.25 cm, counting with piping. The transverse ends of the buttonholes should be parallel to the bevel of the front ends of the collar. Installed metal insignia for positions and badges according to the established encryption are placed on the buttonholes. […] Basically, the type B flyshirt […] differs from the type A flyshirt in that the type B flyshirt has an elongated bar in all heights by 4 cm; hook and loop for fastening the collar and three through loops on the top placket […]. Three small all-army buttons are sewn onto the lower bar in the places corresponding to the loops. A hook is sewn into the right end of the collar, and a loop into the left end.
Military uniform of the Red Army (1936-1945)
Changes and innovations were carried out on the basis of the experience gained from the Winter War with Finland in 1939-40, which gave impetus to a number of changes. Of the entire order, the following were made public: the transition to a single color of uniforms, the introduction of new, more popular and common fabrics, and the gradual introduction of beautiful parade uniforms in combat units.
Norms of supply established for peacetime and wartime were not subject to disclosure. According to these norms, the uniforms that were to be accumulated by the beginning of the mobilization deployment of the army consisted of: khaki caps (in winter - a cap with earflaps of the 1940 model
up to 40, and even in the winter of 41
Cloth shirt with welt pockets, model 1931 for all branches of the military. Cloth shirt consists of the following parts: the front part, in the middle having a strap, fastened with three through loops on three metal buttons with a Red Army star, a back, a stand-up collar, fastened in the middle with two metal hooks, two breast pocket flaps, fastened to a Red Army shirt button, sleeves without folds at the bottom with cuffs fastened with two loops on two Red Army buttons.
Valves pro-carved internal pockets. Canceled by order of the People's Commissar of Defense of the USSR No. 25 of January 15, 1943. The entire composition of the Red Army to switch to new insignia - shoulder straps in the period from February 1 to February 15, 1943.
Artillery uniform 1941 1945
Red Army, medical staff uniform 1943 Most of the medical staff were women. Navy blue berets and skirts had been part of the full dress uniform for the Red Army since the pre-war days, with khaki being assigned in May and August 1942, but most women used the standard men's uniform, or wore mixed clothing that was more comfortable.
76 women were awarded the title, "Hero Soviet Union”, many of them posthumously. From September 16, 1944, sergeants and Red Army soldiers were also officially allowed to have breast welt pockets, but only if they received officer uniforms unfit for wear after putting it in order. Major General, Army 1943-44 Combinations of uniforms from various time periods were quite common during the war.
There is a lot of information on the Soviet uniform and equipment on the Internet, but it is scattered and unsystematic. A few years ago, I started to be interested in Soviet uniforms and equipment, then it grew into an article. Of course, I am far from being the ultimate truth, so I will be glad if more knowledgeable people correct and supplement the article. Also, I did not consider emblems and insignia.
A little history first. Even before the First World War, a uniform appeared in the Russian army, consisting of a protective color of trousers, a shirt-tunic, an overcoat and boots. We have seen her more than once in films about the Civil and Great Patriotic Wars.
Soviet uniform from World War II.
Since then, several uniform reforms have been carried out, but they mainly affected only the dress uniform. “In uniforms, edgings, epaulettes, buttonholes” changed, and the field uniform remained practically unchanged.
In 1969, the field uniform was finally replaced. The cut of trousers has changed, they have become less baggy. The tunic was replaced with a fully unbuttoned tunic. According to one version, the replacement of a tunic with a tunic was caused by the need to decontaminate clothes in case nuclear war. It is dangerous for health to remove a radioactive tunic over the head, so it was recommended to tear it apart, rendering it unusable, which was an unjustified waste of property. The tunic could be unbuttoned and removed without loss. 

The tunic of the 1943 model and the closed tunic of the 1969 model.
The form was sewn from dense cotton fabric. The trousers had two regular slit pockets on the side, the tunic had two slit pockets at the bottom. Compared to modern types of uniforms, and even by Western standards of that time, this is very small. Shiny buttons and cockades, as well as colored epaulettes, were to be replaced with green ones in wartime.

Soviet uniform and equipment of the 1969 model. Live illustration of the Rules for wearing military uniforms. Trousers, tunic, cap, boots. Equipment: Leatherette shoulder strap. On the belt pouch for shops (under right hand fighter) and a grenade (under the left hand), a bayonet-knife. On the shoulders - the straps of a duffel bag with a chest jumper (form the letter H). Diagonally across the chest is the strap of a gas mask bag.

Soviet uniform and equipment of the 1969 model. On the back is a duffel bag. A large bag on the side is a gas mask.





Tarpaulin boots


A guide to shoe care.
The main footwear was tarpaulin boots with footcloths. Kirza is, roughly speaking, a rubberized tarpaulin. This material was developed before the Great Patriotic War to save leather. The top of the boot is sewn from tarpaulin. The lower part, a kind of "galosh", is sewn from leather, because. when walking, significant loads fall on it, which the tarpaulin will not withstand.

Underwear was in the form of a shirt with long sleeves and long underpants made of white fabric, the so-called. "beluga". In summer it was made of thin cotton, in winter it was made of flannel. Such underwear is still found in the army.

The headdress is a cap.
The cap appeared at the beginning of the 20th century, when military aviation began to emerge. Initially, it was called the "folding pilot's hat." A soldier cannot be without a headdress. Caps were the main headgear then. But the pilots in flight put on a leather flight helmet, and the cap had to be put somewhere. The cap could easily be folded up and slipped into a pocket. Subsequently, the cap became a massive soldier's headdress due to its simplicity and cheapness.


In winter - an overcoat and a hat with earflaps.

Work uniform
There was also a work uniform. It was intended for dirty work such as construction, loading and unloading, or repair of equipment. The winter version - a wadded jacket and trousers, reminiscent of a collective farm sweatshirt - could also be worn as a field

Winter work jacket
There were also more advanced pieces of clothing.
Soldiers of the Second World War 20 - Artilleryman of the Red Army in summer field uniform, 1941
Soldiers of the Great Patriotic War #20 - Artilleryman of the Red Army in summer field uniform, 1941- in Russia, the issue was released on 10/09/2013.
The uniform of ordinary artillery units of the Red Army almost completely corresponded to the set of uniforms and equipment of military personnel of rifle divisions.

Soldiers of the Great Patriotic War 20 - Artilleryman of the Red Army, magazine and tin soldier packaged.
The artillery of the Workers 'and Peasants' Red Army was subdivided into military - battalion, regimental, divisional and corps, and artillery of the reserve of the High Command. On the eve of the Great Patriotic War, the military artillery of the Red Army received a stable and fairly effective organization that made it possible to make the most of all resources in both offensive and defensive combat.
However, on initial stage war potential inherent in organizational structure of the Soviet military artillery, was not fully implemented, since many units and subunits were either in the process of formation, or had a significant shortage of material and technical means and personnel.
In the first years after the creation of the Workers 'and Peasants' Red Army for artillery, insignia were introduced from orange, then from red cloth. But already in 1922-1924, traditional insignia were returned to Soviet artillerymen - black with a red edging. Moreover, the royal emblem of the military branch was preserved - crossed gun barrels, which was used in the Russian Imperial Army from the beginning of the 19th century.
GUNNER'S EMBLEM
 According to the Rules for wearing the uniform of the Red Army, introduced in December 1936, emblems by type of troops (services, specialties) were golden in color and were located along the edges of the buttonholes of the tunic, near the transverse edging, and on the upper edge of the overcoat buttonholes, almost close to the corner piping. Since 1940, by Order of the NPO of the USSR No. 391 of November 2, buttonholes of a new type were introduced for the Red Army and junior commanding staff of the Red Army. The buttonhole emblem of the military branch of the corporals and junior commanding officers was located below the golden metal triangle located in the upper corner of the buttonhole, on a red longitudinal cloth gap.
According to the Rules for wearing the uniform of the Red Army, introduced in December 1936, emblems by type of troops (services, specialties) were golden in color and were located along the edges of the buttonholes of the tunic, near the transverse edging, and on the upper edge of the overcoat buttonholes, almost close to the corner piping. Since 1940, by Order of the NPO of the USSR No. 391 of November 2, buttonholes of a new type were introduced for the Red Army and junior commanding staff of the Red Army. The buttonhole emblem of the military branch of the corporals and junior commanding officers was located below the golden metal triangle located in the upper corner of the buttonhole, on a red longitudinal cloth gap.
The emblem of artillery - all the same crossed cannon barrels - was established by order of the NPO of the USSR No. 33 of March 10, 1936, and exemplary drawings of lapel badges-emblems were published in the Charter of the Internal Service of the Red Army (UVS-37) in 1938. Initially, it was assumed that metal emblems would only be worn by command staff and cadets of military schools, and on the buttonholes of privates and sergeants they had to be applied with stenciled paint. In practice, the application of emblems with paint was practically not used. 
In addition, it should be emphasized that the color of the buttonholes and edging was determined by the type of troops a given unit belongs to, and the emblem corresponded to the specialty of specific servicemen of the unit. That is, the military personnel of an artillery battery consisting of rifle regiment wore crimson buttonholes of the infantry with artillery emblems. At the same time, the Red Army artillery regiments or individual divisions in the rifle division wore black with red edging buttonholes.
However, after the start of the Great Patriotic War, by Order of the NPO of the USSR No. 253 of August 1, 1941, the wearing of all sleeve insignia, colored buttonholes and insignia for all categories of military personnel was canceled: buttonholes, emblems and insignia of a protective color were installed. True, in practice this order was implemented only by the end of 1942.
ANNOUNCEMENT Soldiers of the Great Patriotic War №21- Major General of Aviation in summer uniforms, 1941

Artillery has long played an important role in the army of Moscow Russia. Despite the difficulties with the transportation of guns in the eternal Russian impassability, the main attention was paid to the casting of heavy guns and mortars - guns that could be used in the siege of fortresses.
Under Peter I, some steps towards the reorganization of artillery were taken as early as 1699, but only after the Narva defeat did it begin in all seriousness. The guns began to be reduced to batteries, intended for field battles, the defense of fortresses and for sieges. According to the Charter of 1701, temporary batteries began to be reduced to the Artillery Regiment, which also included engineering units.
In addition to gunners and scorers, the Artillery Regiment included miners, engineers, pontoons and pioneers.
artillery regiment included:
one bombardment company (113 people),
six gunnery companies (152 soldiers and officers each),
one company of miners (75 people).
In addition, the staff had 25 engineers, 36 pontoons, 6 firecrackers, and 19 people were part of the headquarters.
Bombardiers served howitzers and mortars, gunners - guns. Both of them were supposed to have handguns. The gunners were armed with fuzei, and the bombardiers with hand mortars. This weapon had a short barrel (length 250 mm, caliber 74 mm), mounted on a rifle-type butt; the shot was fired with a flintlock.
They fired mortars with one- and three-pound grenades.
Many of the drawings showing how mortars are fired show soldiers resting the barrel of a weapon on a halberd and resting the butt against their shoulder. In fact, however, due to the extreme force of the recoil, this was rarely done. Much more often, they fired from mortars, resting the butt on the ground and giving the weapon the desired slope “by eye”.

By 1723, it was possible to significantly streamline the calibers of Russian artillery. Now, apart from the fortress guns, the army had six 6-pounder, twelve 8-pounder, three 12-pounder guns and four 20-pounder mortars.
The regimental artillery consisted of 80 three-pounder guns. In siege artillery, 30 18- and 24-pounder guns and 100 Kugornov mortars. These last guns, named after their inventor (Dutch engineer Kuhorn), could fire 6-pounder grenades up to 400 paces.
"Kugornovy" mortars were installed on wooden bases in the form of a massive rectangular frame. The total weight of the system did not exceed 42 kilograms; in addition, the barrel was easily removed from the base, so that the gun turned out to be quite mobile.
Interestingly, such mortars were in service with the Russian army for more than 200 (!) Years - they were successfully used in the First World War, and were replaced only by mortars ...
A huge influence on the process of reorganization of Russian artillery in the era of Peter the Great was exerted by Feldzekhmeister General and Artillery Commander Count James William Bruce (in Russia he was called Yakov Vilimovich).
The merit of Bruce was:
establishment of the Artillery Regiment;
division of artillery into field and siege artillery;
the introduction of the "Hartmann artillery scale" into the practice of Russian artillery, which made it possible to standardize the types of guns and bring them to a single system.
Cut uniform gunners of the army of Peter the Great was the same as in the infantry. Caftans, camisoles and pantaloons relied on red, with cornflower-blue cuffs and loop lining.
Stockings could be either white or white with vertical blue stripes.
Both black cocked hats and caps served as headdresses - more often red with blue trim.

| 1 |
Bombardier of the Artillery Regiment. |
| 2, 3 |
Gunners of the Artillery Regiment. |
| 4 |
Junior Officer of the Artillery Regiment. |
| Information: "Cavalry of Peter the Great" (New Soldier No. 190) | |
Complemented uniform black ties and cornflower blue epanchi.
The scorers wore "shishaki" hats similar to the corresponding hats grenadier of the guard, but without a plume of feathers and without a nape.
Since 1720 a uniform, as in the infantry, has been changed. Uniforms have become somewhat simpler in cut. The color is still red; collar - red, turndown. Cuffs and lining of loops - blue. Camisole and trousers are red, ties and stockings are white. Black cocked hats began to be sheathed along the edge with white galloon.
A uniform officers, as in the whole army, was not specified. According to various sources, artillery officers wore uniform, similar to a soldier's, but with red cuffs trimmed with gold galloon.
Scarves - like those of infantry officers, but gunners sometimes tied them around the waist. Artillery officers were highly respected; they had an advantage of one rank over infantry and cavalry officers, and accordingly received a salary one rank above their real rank.
Source: website A uniform armies of the world - //uniforma-army.ru/
Ask a Question
Show all reviews 0Read also
Military uniforms in Russia, as in other countries, arose earlier than all others. The main requirements that they had to satisfy were functional convenience, uniformity in the branches and types of troops, a clear difference from the armies of other countries. The attitude to the military uniform in Russia has always been very interested and even loving. The uniform served as a reminder of military prowess, honor and high feeling military partnership. It was believed that the military uniform was the most elegant and attractive
Not only historical documents, but also works of art, which take us to the pre-revolutionary past, are filled with examples of the relationship between servicemen of different ranks. The lack of understanding of a single gradation does not prevent the reader from isolating the main theme of the work, however, sooner or later, one has to think about the difference between the addresses Your Honor and Your Excellency. Few people notice that in the army of the USSR the appeal was not abolished, it was only replaced by a single one for all
The gorget is a crescent-shaped metal plate approximately 20x12 cm in size, suspended horizontally by the ends on the officer's chest near the throat. Designed to determine the rank of an officer. More often in the literature it is referred to as an officer's badge, neck badge, officer's badge. However, the correct name for this element of military clothing is gorget. In some publications, in particular in the book A. Kuznetsov Awards, the gorget is mistakenly considered a collective award sign. However, this
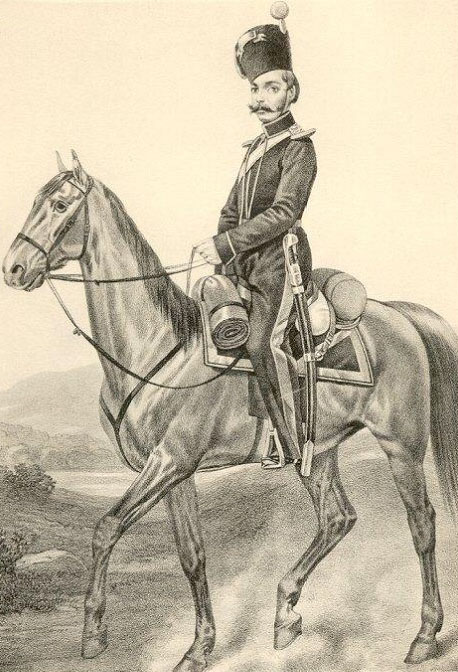 Until April 6, 1834, they were called companies. January 1827, 1 day - On officer epaulettes, to distinguish ranks, forged stars were installed, as at that time introduced in regular troops 23. July 10, 1827 - In the Don horse artillery companies, round pompoms are installed at the lower ranks of red wool, officers have silver drawings 1121 and 1122 24 . 1829 August 7 days - Epaulettes on officer uniforms are installed with a scaly field, following the model
Until April 6, 1834, they were called companies. January 1827, 1 day - On officer epaulettes, to distinguish ranks, forged stars were installed, as at that time introduced in regular troops 23. July 10, 1827 - In the Don horse artillery companies, round pompoms are installed at the lower ranks of red wool, officers have silver drawings 1121 and 1122 24 . 1829 August 7 days - Epaulettes on officer uniforms are installed with a scaly field, following the model
A document regarding the clothing of the army, filed by General Field Marshal Prince Grigory Potemkin-Tavrichesky in the name of the Highest Name in 1782 as far as his prosperity, he weighed himself down with iron armor of protection, such protection even extended to horses; then, undertaking long trips and forming squadrons, they began to lighten themselves; full armor changed into half and
Espanton protazan, halberd Espanton, protazan partisan, halberd are actually ancient weapons of the pole type. Espanton and pierced weapons are piercing, and the halberd is piercing and chopping. By the end of the 17th century, with the development of firearms, they were all hopelessly outdated. It is difficult to say what Peter I was guided by when introducing these antiquities into service with non-commissioned officers and infantry officers of the newly created Russian Army. Most likely on the model of Western armies. As weapons, they played no role,
The clothing of military personnel is established by decrees, orders, rules or special normative acts. Wearing the naval uniform of the naval uniform is mandatory for military personnel armed forces state and other formations where it is provided military service. In the armed forces of Russia, there are a number of accessories that were in the naval uniform of the times Russian Empire. These include shoulder straps, boots, long overcoats with buttonholes.
Continuity and innovation in modern military heraldry Russian Federation the emblem of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation in the form of a golden double-headed eagle with outstretched wings, holding a sword in its paws, as the most common symbol of the armed defense of the Fatherland, and a wreath, a symbol of special importance, significance and honor of military labor. This emblem was established to mark the belonging
In Russia, the name of Tsar Peter I is associated with numerous reforms and transformations that radically changed the patriarchal structure of civil society. Wigs replaced beards, shoes and over the knee boots replaced bast shoes and boots, caftans gave way to European dresses. The Russian army, also under Peter I, did not stand aside and gradually switched to the European equipment system. One of the main elements of the uniform is the military uniform. Each branch of the military receives its own uniform,
Considering all the stages of the creation of the Russian armed forces, it is necessary to delve deeply into history, and even in the days of the principalities in question about the Russian empire, and even more so about the regular army, the emergence of such a thing as defense capability begins precisely from this era. In the XIII century, Russia was represented by separate principalities. Although their military squads were armed with swords, axes, spears, sabers and bows, they could not serve as a reliable defense against extraneous encroachments. United army
Officers of the Cossack troops, who are under the Office of the Military Ministry, full dress and festive uniforms. May 7, 1869. The Life Guards Cossack Regiment marching uniform. September 30, 1867. Generals in the army Cossack units full dress. March 18, 1855 Adjutant General, listed in the Cossack units in full dress. March 18, 1855 Adjutant wing, listed in the Cossack units in full dress. March 18, 1855 Chief officers
 The accession to the throne of Emperor Alexander I was marked by a change in the uniform of the Russian army. The new uniform combined fashion trends and traditions of Catherine's reign. The soldiers dressed in tailcoat-style uniforms with high collars, boots replaced all ranks with boots. Jaegers of the light infantry received hats with a brim, reminiscent of civilian top hats. A characteristic detail of the new uniforms of heavy infantry soldiers was a leather helmet with a high plume.
The accession to the throne of Emperor Alexander I was marked by a change in the uniform of the Russian army. The new uniform combined fashion trends and traditions of Catherine's reign. The soldiers dressed in tailcoat-style uniforms with high collars, boots replaced all ranks with boots. Jaegers of the light infantry received hats with a brim, reminiscent of civilian top hats. A characteristic detail of the new uniforms of heavy infantry soldiers was a leather helmet with a high plume.
They do not emit a warlike roar, they do not sparkle with a polished surface, they are not decorated with chased coats of arms and plumes, and quite often they are generally hidden under jackets. However, today, without this armor, unsightly in appearance, it is simply unthinkable to send soldiers into battle or ensure the safety of VIPs. Body armor is clothing that prevents bullets from entering the body and therefore protects a person from being shot. It is made from materials that scatter
The shoulder straps of the tsarist army of 1914 are rarely mentioned in feature films and historical books. Meanwhile, this is an interesting object of study in the imperial age, during the reign of Tsar Nicholas II, uniforms were an object of art. Before the start of the First World War, the distinctive signs of the Russian army differed significantly from those that are used now. They were brighter and contained more information, but at the same time they did not have functionality and were easily visible in the field.
Very often in cinema and classical literature there is the title of lieutenant. Now there is no such rank in the Russian army, so many people are interested in the lieutenant, what is the rank in accordance with modern realities. To understand this, we need to look at history. The history of the appearance of the rank Such a rank as a lieutenant still exists in the army of other states, but it does not exist in the army of the Russian Federation. It was first adopted in the 17th century in regiments brought to the European standard.
 THE EMPEROR, on the 22nd day of February and the 27th day of October of this year, the Highest command deigned to 1. Generals, Headquarters and Chief Officers and lower ranks of all Cossack troops, except for the Caucasian, and except for the Guards Cossack units, as well as civil officials consisting in the service in the Cossack troops and in the regional boards and administrations in the service of the Kuban and Terek regions, named in articles 1-8 of the attached list, Appendix 1, to have a uniform according to the attached hereto
THE EMPEROR, on the 22nd day of February and the 27th day of October of this year, the Highest command deigned to 1. Generals, Headquarters and Chief Officers and lower ranks of all Cossack troops, except for the Caucasian, and except for the Guards Cossack units, as well as civil officials consisting in the service in the Cossack troops and in the regional boards and administrations in the service of the Kuban and Terek regions, named in articles 1-8 of the attached list, Appendix 1, to have a uniform according to the attached hereto
 The army is the armed organization of the state. Consequently, the main difference between the army and other state organizations is that it is armed, that is, to perform its functions it has a complex various kinds weapons and means for their use. In 1812, the Russian army was armed with cold and firearms, as well as protective weapons. To edged weapons, the combat use of which is not related to the use of explosives for the period under review -
The army is the armed organization of the state. Consequently, the main difference between the army and other state organizations is that it is armed, that is, to perform its functions it has a complex various kinds weapons and means for their use. In 1812, the Russian army was armed with cold and firearms, as well as protective weapons. To edged weapons, the combat use of which is not related to the use of explosives for the period under review -
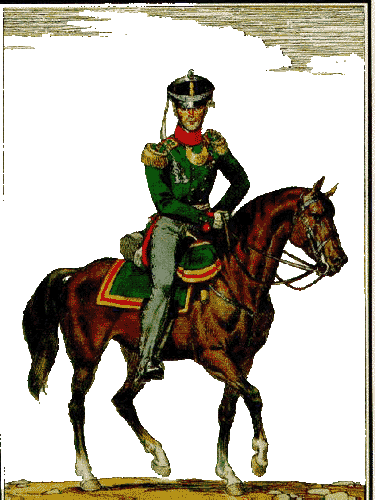 Almost all the countries of Europe were drawn into the wars of conquest, which were continuously waged by the Emperor of France Napoleon Bonaparte at the beginning of the last century. For a short historical period of 1801-1812, he managed to subjugate almost the entire Western Europe but that wasn't enough for him. The emperor of France claimed world domination, and Russia became the main obstacle on his way to the top of world glory. In five years I will be the master of the world, he declared in an ambitious impulse,
Almost all the countries of Europe were drawn into the wars of conquest, which were continuously waged by the Emperor of France Napoleon Bonaparte at the beginning of the last century. For a short historical period of 1801-1812, he managed to subjugate almost the entire Western Europe but that wasn't enough for him. The emperor of France claimed world domination, and Russia became the main obstacle on his way to the top of world glory. In five years I will be the master of the world, he declared in an ambitious impulse,
 AT Patriotic War 1812, 107 Cossack regiments and 2.5 Cossack horse artillery companies participated. They constituted irregular searches, that is, part of the armed forces that did not have a permanent organization and differed from regular military formations in recruitment, service, training, and uniforms. The Cossacks were a special military estate, which included the population of certain territories of Russia, which constituted the corresponding Cossack army of the Don, Ural, Orenburg,
AT Patriotic War 1812, 107 Cossack regiments and 2.5 Cossack horse artillery companies participated. They constituted irregular searches, that is, part of the armed forces that did not have a permanent organization and differed from regular military formations in recruitment, service, training, and uniforms. The Cossacks were a special military estate, which included the population of certain territories of Russia, which constituted the corresponding Cossack army of the Don, Ural, Orenburg,
 The Russian army, which owns the honor of victory over the Napoleonic hordes in the Patriotic War of 1812, consisted of several types of armed forces and military branches. The types of armed forces included ground forces and Navy. Ground troops included several branches of the army infantry, cavalry, artillery and pioneers, or engineers now sappers. The invading troops of Napoleon on the western borders of Russia were opposed by 3 Russian armies of the 1st Western under the command
The Russian army, which owns the honor of victory over the Napoleonic hordes in the Patriotic War of 1812, consisted of several types of armed forces and military branches. The types of armed forces included ground forces and Navy. Ground troops included several branches of the army infantry, cavalry, artillery and pioneers, or engineers now sappers. The invading troops of Napoleon on the western borders of Russia were opposed by 3 Russian armies of the 1st Western under the command
In the reign of Alexander III there were no wars or major battles. All solutions for foreign policy received personally by the Sovereign. The post of state chancellor was even abolished. In foreign policy Alexander III took a course towards rapprochement with France, and in the construction of the army, much attention was paid to recreating the naval power of Russia. The emperor understood that the absence of a strong fleet had deprived Russia of a significant part of its great-power weight. During his reign, the foundation was laid
 The science of ancient Russian weapons has a long tradition; it originated from the moment of discovery in 1808 at the site of the famous Lipitsk battle in 1216, a helmet and chain mail, possibly belonging to Prince Yaroslav Vsevolodovich. Historians and experts in the study of ancient weapons of the last century A. V. Viskovatov, E. E. Lenz, P. I. Savvaitov, N. E. Brandenburg attached considerable importance to the collection and classification of items of military equipment. They also began decoding and its terminology, including -. neck
The science of ancient Russian weapons has a long tradition; it originated from the moment of discovery in 1808 at the site of the famous Lipitsk battle in 1216, a helmet and chain mail, possibly belonging to Prince Yaroslav Vsevolodovich. Historians and experts in the study of ancient weapons of the last century A. V. Viskovatov, E. E. Lenz, P. I. Savvaitov, N. E. Brandenburg attached considerable importance to the collection and classification of items of military equipment. They also began decoding and its terminology, including -. neck
 1. PRIVATE GRENADER REGIMENT. 1809 Selected soldiers, designed to throw hand grenades during the siege of fortresses, first appeared during the Thirty Years' War 1618-1648. The grenadier units selected people of high stature, distinguished by their courage and knowledge of military affairs. In Russia, from the end of the 17th century, grenadiers were placed at the head of assault columns, to strengthen the flanks and to act against cavalry. To early XIX centuries, the grenadiers turned into a kind of elite troops that did not differ in weapons
1. PRIVATE GRENADER REGIMENT. 1809 Selected soldiers, designed to throw hand grenades during the siege of fortresses, first appeared during the Thirty Years' War 1618-1648. The grenadier units selected people of high stature, distinguished by their courage and knowledge of military affairs. In Russia, from the end of the 17th century, grenadiers were placed at the head of assault columns, to strengthen the flanks and to act against cavalry. To early XIX centuries, the grenadiers turned into a kind of elite troops that did not differ in weapons
 A military uniform is not only clothing that is supposed to be comfortable, durable, practical and light enough so that a person carrying the hardships of military service is reliably protected from the vicissitudes of weather and climate, but also a kind of visiting card of any army. Since the uniform appeared in Europe in the 17th century, the representative role of the uniform has been very high. The uniform in the old days spoke about the rank of its wearer and what kind of troops he belonged to, or even
A military uniform is not only clothing that is supposed to be comfortable, durable, practical and light enough so that a person carrying the hardships of military service is reliably protected from the vicissitudes of weather and climate, but also a kind of visiting card of any army. Since the uniform appeared in Europe in the 17th century, the representative role of the uniform has been very high. The uniform in the old days spoke about the rank of its wearer and what kind of troops he belonged to, or even
His Imperial Majesty's Own Convoy was the formation of the Russian guard, which carried out the protection of the royal person. The main core of the convoy were the Cossacks of the Terek and Kuban Cossack troops. Circassians, Nogays, Stavropol Turkmens, other mountaineers-Muslims of the Caucasus, Azerbaijanis, a team of Muslims, since 1857 the fourth platoon of the Life Guards of the Caucasian squadron, Georgians, Crimean Tatars, other nationalities of the Russian Empire. The official date of the founding of the convoy
 From the author. This article provides a brief excursion into the history of the emergence and development of uniforms of the Siberian Cossack army. The Cossack form of the era of the reign of Nicholas II is considered in more detail - the form in which the Siberian Cossack army went down in history. The material is intended for novice historians-uniformists, military-historical reenactors and for modern Siberian Cossacks. In the picture on the left is the military sign of the Siberian Cossack army
From the author. This article provides a brief excursion into the history of the emergence and development of uniforms of the Siberian Cossack army. The Cossack form of the era of the reign of Nicholas II is considered in more detail - the form in which the Siberian Cossack army went down in history. The material is intended for novice historians-uniformists, military-historical reenactors and for modern Siberian Cossacks. In the picture on the left is the military sign of the Siberian Cossack army
The uniform of the army hussars of the Russian Imperial Army of 1741-1788 the army had little need for regular light cavalry. The first official hussar units in the Russian army appeared during the reign of the Empress
 The uniform of the army hussars of the Russian Imperial Army of 1796-1801 In the previous article, we talked about the uniform of the Russian army hussars during the reign of Empresses Elizabeth Petrovna and Catherine II from 1741 to 1788. After Paul I ascended the throne, he revived the army hussar regiments, but introduced Prussian-Gatchina motifs into their uniforms. Moreover, from November 29, 1796, the names of the hussar regiments became the former name by the name of their chief
The uniform of the army hussars of the Russian Imperial Army of 1796-1801 In the previous article, we talked about the uniform of the Russian army hussars during the reign of Empresses Elizabeth Petrovna and Catherine II from 1741 to 1788. After Paul I ascended the throne, he revived the army hussar regiments, but introduced Prussian-Gatchina motifs into their uniforms. Moreover, from November 29, 1796, the names of the hussar regiments became the former name by the name of their chief
The uniform of the hussars of the Russian Imperial Army of 1801-1825 In the two previous articles we talked about the uniform of the Russian army hussars of 1741-1788 and 1796-1801. In this article we will talk about the hussar uniform of the reign of Emperor Alexander I. So, let's get started ... On March 31, 1801, all the hussar regiments of the army cavalry were given the following names: hussar regiment, new name Melissino
Uniform of the hussars of the Russian Imperial Army of 1826-1855 We continue the series of articles on the uniform of the Russian army hussar regiments. In previous articles, we reviewed the hussar uniforms of 1741-1788, 1796-1801 and 1801-1825. In this article we will talk about the changes that occurred during the reign of Emperor Nicholas I. In 1826-1854, the following hussar regiments were renamed, created or disbanded.
 Uniform of the hussars of the Russian Imperial Army of 1855-1882 We continue the series of articles on the uniform of the Russian army hussar regiments. In previous articles, we got acquainted with the hussar uniform of 1741-1788, 1796-1801, 1801-1825 and 1826-1855. In this article we will talk about the changes in the uniform of Russian hussars that took place during the reign of Emperors Alexander II and Alexander III. On May 7, 1855, the following changes were made to the uniform of officers of the army hussars
Uniform of the hussars of the Russian Imperial Army of 1855-1882 We continue the series of articles on the uniform of the Russian army hussar regiments. In previous articles, we got acquainted with the hussar uniform of 1741-1788, 1796-1801, 1801-1825 and 1826-1855. In this article we will talk about the changes in the uniform of Russian hussars that took place during the reign of Emperors Alexander II and Alexander III. On May 7, 1855, the following changes were made to the uniform of officers of the army hussars
 The uniform of the hussars of the Russian Imperial Army of 1907-1918 We are finishing a series of articles on the uniform of the Russian army hussars of 1741-1788, 1796-1801, 1801-1825, 1826-1855 and 1855-1882. In the last article of the cycle, we will talk about the uniform of the restored army hussars in the reign of Nicholas II. From 1882 to 1907, there were only two hussar regiments in the Russian Empire, both in the Imperial Guard of the Life Guards, His Majesty's Hussar Regiment and the Life Guards of the Grodno
The uniform of the hussars of the Russian Imperial Army of 1907-1918 We are finishing a series of articles on the uniform of the Russian army hussars of 1741-1788, 1796-1801, 1801-1825, 1826-1855 and 1855-1882. In the last article of the cycle, we will talk about the uniform of the restored army hussars in the reign of Nicholas II. From 1882 to 1907, there were only two hussar regiments in the Russian Empire, both in the Imperial Guard of the Life Guards, His Majesty's Hussar Regiment and the Life Guards of the Grodno
 There is a version that the forerunner of the Lancers was the light cavalry of the army of the conqueror Genghis Khan, whose special detachments were called oglans and were used mainly for reconnaissance and outpost service, as well as for sudden and swift attacks on the enemy in order to disrupt his ranks and prepare an attack on the main forces. An important part of the weapons of the oglans were pikes, decorated with weathervanes. In the reign of Empress Catherine II, it was decided to form a regiment that seems to contain
There is a version that the forerunner of the Lancers was the light cavalry of the army of the conqueror Genghis Khan, whose special detachments were called oglans and were used mainly for reconnaissance and outpost service, as well as for sudden and swift attacks on the enemy in order to disrupt his ranks and prepare an attack on the main forces. An important part of the weapons of the oglans were pikes, decorated with weathervanes. In the reign of Empress Catherine II, it was decided to form a regiment that seems to contain
 1 Don Ataman, XVII century The Don Cossacks of the XVII century consisted of old Cossacks and Golota. The old Cossacks were those who came from the Cossack families of the 16th century and were born on the Don. Golota was called the Cossacks in the first generation. Golota, who was lucky in battles, grew rich and became old Cossacks. Expensive fur on a hat, a silk caftan, a zipun from bright overseas cloth, a saber and a firearm - a squeaker or a carbine were indicators
1 Don Ataman, XVII century The Don Cossacks of the XVII century consisted of old Cossacks and Golota. The old Cossacks were those who came from the Cossack families of the 16th century and were born on the Don. Golota was called the Cossacks in the first generation. Golota, who was lucky in battles, grew rich and became old Cossacks. Expensive fur on a hat, a silk caftan, a zipun from bright overseas cloth, a saber and a firearm - a squeaker or a carbine were indicators
 Military uniforms are called clothes established by rules or special decrees, the wearing of which is mandatory for any military unit and for each branch of the military. The form symbolizes the function of its bearer and his belonging to the organization. The stable phrase honor of the uniform means military or corporate honor in general. Even in the Roman army, soldiers were given the same weapons and armor. In the Middle Ages, it was customary to depict the coat of arms of a city, kingdom or feudal lord on shields,
Military uniforms are called clothes established by rules or special decrees, the wearing of which is mandatory for any military unit and for each branch of the military. The form symbolizes the function of its bearer and his belonging to the organization. The stable phrase honor of the uniform means military or corporate honor in general. Even in the Roman army, soldiers were given the same weapons and armor. In the Middle Ages, it was customary to depict the coat of arms of a city, kingdom or feudal lord on shields,
 The goal of the Russian Tsar Peter the Great, to which all the economic and administrative resources of the empire were subordinated, was the creation of the army as the most effective state machine. The army, which was inherited by Tsar Peter, hardly perceived military science modern Europe, the army can be called a stretch, and the cavalry in it was much less than in the armies of the European powers. The words of one of the Russian noblemen of the late 17th century are known. It is a shame to look at the cavalry of the horse
The goal of the Russian Tsar Peter the Great, to which all the economic and administrative resources of the empire were subordinated, was the creation of the army as the most effective state machine. The army, which was inherited by Tsar Peter, hardly perceived military science modern Europe, the army can be called a stretch, and the cavalry in it was much less than in the armies of the European powers. The words of one of the Russian noblemen of the late 17th century are known. It is a shame to look at the cavalry of the horse
From the author. In this article, the author does not claim to fully cover all issues related to the history, uniform, equipment and structure of the Russian army cavalry, but only tried to briefly talk about the types of uniforms in 1907-1914. Those who wish to get more deeply acquainted with the uniform, way of life, customs and traditions of the Russian army cavalry can refer to the primary sources given in the bibliography for this article. Dragoons At the beginning of the 20th century, the Russian cavalry was considered
The corps of military topographers was created in 1822 with the aim of topographic topographic and geodetic support of the armed forces, carrying out state cartographic surveys in the interests of both the armed forces and the state as a whole, under the leadership of the military topographic depot of the General Staff, as a single customer of cartographic products in the Russian Empire . Chief officer of the Corps of military topographers in a semi-caftan of the times
At the very end of the XVII century. Peter I decided to reorganize the Russian army according to the European model. The basis for the future army was the Preobrazhensky and Semenovsky regiments, which already in August 1700 formed the Royal Guard. The uniform of the soldiers of the Fusiliers of the Life Guards of the Preobrazhensky Regiment consisted of a caftan, camisole, trousers, stockings, shoes, a tie, a hat and an epanchi. The caftan, see the image below, is made of dark green cloth, knee-length, instead of a collar it had a cloth
During the First World War of 1914-1918, in the Russian Imperial Army, the tunic of arbitrary imitation models of English and French models, which received the general name French after the name of the English General John French, became widespread. The design features of the service jackets mainly consisted in the design of a soft turn-down collar, or a soft standing collar with a button closure, like the collar of a Russian tunic, adjustable cuff width with the help of
 1 Half head of Moscow archers, 17th century In the middle of the 17th century, Moscow archers formed a separate corps within the streltsy army. Organizationally, they were divided into orders of the regiment, which were headed by head colonels and half-heads by majors lieutenant colonels. Each order was divided into hundreds of companies, commanded by centurion captains. Officers from the head to the centurion were appointed by their decree from the tsar from the nobility. The companies, in turn, were divided into two platoons of fifty
1 Half head of Moscow archers, 17th century In the middle of the 17th century, Moscow archers formed a separate corps within the streltsy army. Organizationally, they were divided into orders of the regiment, which were headed by head colonels and half-heads by majors lieutenant colonels. Each order was divided into hundreds of companies, commanded by centurion captains. Officers from the head to the centurion were appointed by their decree from the tsar from the nobility. The companies, in turn, were divided into two platoons of fifty
In the first half of 1700, 29 infantry regiments were formed, and in 1724 their number increased to 46. The uniform of the army field infantry regiments did not differ in cut from the guards, but the colors of the cloth from which the caftans were sewn were extremely colorful. In some cases, soldiers of the same regiment were dressed in uniforms of different colors. Until 1720, a cap was a very common headdress, see fig. below. It consisted of a cylindrical crown and a band sewn on
