In 2017, a new model of the KIM USE in biology was adopted, aimed at increasing the diversity of the tested aspects of the biological training of graduates.
Each version of the examination paper consists of two parts. Tasks in the variant are presented in continuous numbering mode. The structure of the examination paper has been optimized:
1.
The number of tasks in the examination paper has been reduced from 40 to 28.
2.
In part 1, tasks of new types are proposed, which differ significantly in types learning activities: to fill in the missing elements of a diagram or table, to find errors in a drawing, to analyze and synthesize information, to analyze graphs and tables with statistical data.
3.
The maximum number of primary points has been slightly reduced: from 61 in 2016 to 59 in 2017.
4.
Increased from 180 to 210 minutes the time to complete the work.
In part 2, the number and types of tasks with a detailed answer remained unchanged - 7 tasks.
Particular emphasis is placed on the formation of methods of activity: mastering methodological skills; application of knowledge in explanation biological processes, phenomena, mastering the ability to solve biological problems. Checking the skills of working with information of biological content is carried out through its presentation in various ways (in the form of texts, drawings, diagrams, tables, graphs, diagrams).
In 2017 from the examination USE work in biology, it is planned to exclude all tasks with the choice of one answer. This is due to the presence of the following significant shortcomings in them: the uniformity of the form of presentation of the content being checked, the impossibility of creating tasks of a problematic or creative nature; lack of capacity to test students' skills of a practical nature; difficulty in identifying true gaps in the development of content among USE participants. A significant disadvantage of tasks with a choice of one answer is also the presence of an element of chance, guessing the correct answer.
As shown comparative analysis USE results over the past two years, the reduction in the number of tasks with the choice of one correct answer from 36 to 25 in the examination paper did not lead to a noticeable decrease in the USE results. The proportion of participants in the USE in biology who did not score the minimum number of points remains approximately at the same level, within the limits of statistically acceptable errors.
Significant modernization in terms of the form and structure of KIM required a correction of approaches to the construction of examination work, the inclusion of tasks of a new format.
In part 1 of the new format of the examination paper, only short answer tasks were retained, but their number was increased, and in some cases the form of their presentation was significantly changed compared to previous years. It is known that tasks with a short answer allow not only to check a larger amount of content subject, but most importantly, to provide an assessment of general educational and subject skills (comparison, generalization, classification, systematization, explanation, solution of educational and practical problems, etc.), which corresponds to modern development trends general education.
Along with the preservation of existing tasks, new biological tasks appeared, and the range of tasks with drawings expanded.
As an example of a modernized task, we give task 3 (hereinafter, tasks from the project are given demo version KIM).
This is a calculated biological problem. The task was created on the basis of tasks traditional for KIM USE in biology with a choice of one answer. AT new edition, USE participant, based on the knowledge of genetic information and the chromosome set of somatic and germ cells, independently carries out all the necessary calculations.
As an example of a task for working with a drawing, we give task 4.

A feature of this model of the task is that the certified person is invited to display two of its characteristic feature. Moreover, one of the features given in the task checks the knowledge of the morphology of the object, while the second one checks the knowledge of properties or functions. Such tasks check, in addition to the ability to work with visual information, knowledge in the field of the cell and its vital activity.
Along with well-known or modernized task types in examination paper completely new tasks are included that test the development of the conceptual apparatus by filling in gaps in diagrams, tables, working with graphs, tables, histograms, etc. All of them are aimed at strengthening the activity basis and make the examination work more practice-oriented.
Task 1 can serve as an example of such tasks.

This task allows you to check not only the knowledge of the conceptual apparatus of the biology course, but also the ability to establish the subordination and hierarchy of terms (concepts), as well as their internal logical connection.
Consider examples of tasks (task 21) for working with information presented in graphical or tabular form, a task for analyzing research results.

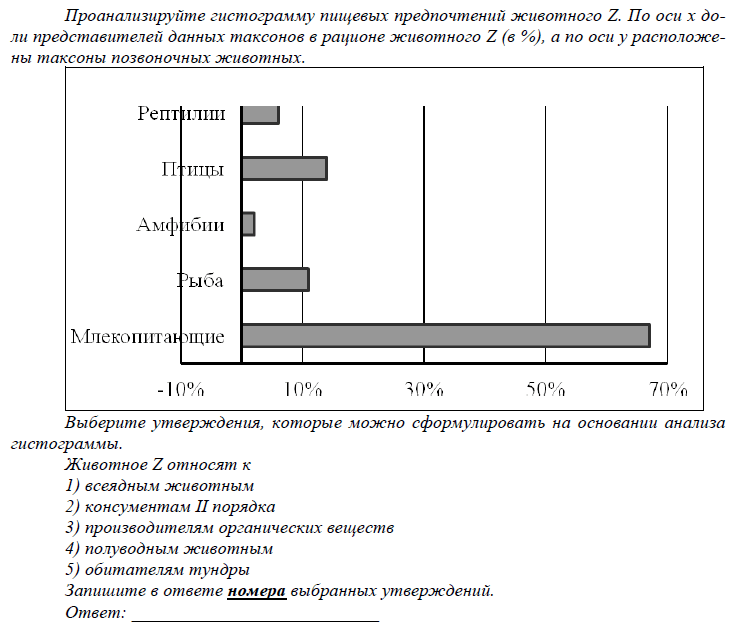
It seems that with the help of such tasks it is possible to ensure the formation of the foundations of a holistic scientific picture of the world and the ability of graduates to analyze, evaluate and generalize scientific information.
The new model of KIM USE is successive with the established model of OGE 9 in biology. Separate types of tasks, which in a modernized form will be included in KIM in 2017, have been successfully tested for many years during the certification of students in basic general education programs and are available in open jar OGE assignments. They can become the basis for preparing students for the exam in biology in the coming academic year.
Task 9 can serve as an example of continuity.

In the OGE, with the help of such tasks, knowledge of the structure, life activity and significance of animal and plant organisms is checked. Bacteria and viruses will be added to these objects in the new KIM USE model.
In general, in the exam model of the USE in 2017, the objects of control, as in previous years, are knowledge and skills that make up the invariant core of the content of the biology course of the main and high school, its sections "Plants", "Bacteria, fungi, lichens", "Animals", "Man and his health", "General biology". These sections are presented in the Codifier in the form of seven content blocks and requirements for the level of training of graduates. educational organizations for a unified state exam 2017 in Biology.
Plan consultations on preparation for the exam in biology
11th grade students of MBOU "Staroilmovskaya secondary school" in the 2016-2017 academic year.
(Biology teacher: Zakharova S.A.)
sectionName
section
Content element.
Kind of activity
Content elements tailored
changes in 2017
the date
Biology is the science of living nature.
Methods of biological science, signs of living things, levels of life organization.
Changes in the exam in biology in 2017
6.09
The cell as a biological system.
Cell theory. Diversity of cells
Cell theory, its main provisions. Cell structure organisms, the similarity of the structure of the cells of all organisms is the basis of unity organic world, proof of the relationship of living nature.
13.09
Structural-functional and chemical organization of the cell.
Chemical organization cells. The relationship of the structure and function of proteins, nucleic acids, ATP, carbohydrates, lipids that make up the cell. Justification of the relationship of organisms based on analysis chemical composition cells.
The structure of pro- and eukaryotic cells. The relationship of the structure and functions of the parts and organelles of the cell is the basis of its integrity.
20.09
Metabolism
Metabolism: energy and plastic metabolism, their relationship. Energy exchange. stages energy metabolism. Enzymes, their chemical nature, role in metabolism. Photosynthesis, its cosmic role. Phases of photosynthesis. Light and dark reactions of photosynthesis, their relationship. The meaning of photosynthesis.
27.09
Cell division. reproduction of organisms.
Chromosomes, their number, shape and size, species constancy. Mitosis is the division of somatic cells. Meiosis. Phases of mitosis and meiosis. The development of germ cells in plants and animals. Determination of the set of chromosomes in somatic and germ cells. Similarities and differences between mitosis and meiosis, their significance.
04.10
III
The body as a biological system.
Diversity of organisms. Viruses.
11.10
reproduction of organisms. Ontogenesis.
18.10
Main genetic concepts. Genetic patterns.
Genetics, its tasks. Basic genetic concepts. Chromosomal theory of heredity. The genotype as an integral system.
25.10
Linked inheritance of traits, violation of the linkage of genes. Sex genetics. Inheritance of sex-linked traits. Solution of genetic problems. Drawing up cross-breeding schemes.
Patterns of heredity. Human genetics.
Patterns of heredity, their cytological basis. Mono- and dihybrid crossing.
01.11
Regularities of variability.
Variability of traits in organisms: modification, mutation, combinative. Types of mutations and their causes. The value of variability in the life of organisms and in evolution. reaction rate.
The harmful effects of mutagens, alcohol, drugs, nicotine on the genetic apparatus of the cell. Protection of the environment from pollution by mutagens. Prevention of human hereditary diseases.
8.11
Selection. Biotechnology. artificial selection.
Biotechnology, cell and genetic engineering, cloning. The value of biotechnology for the development of breeding, National economy, conservation of the planet's gene pool. Evaluation of the ethical aspects of the development of some research in biotechnology (human cloning, directed changes in the genome.)
15.11
Diversity of organisms.
Diversity of organisms. bacteria. Mushrooms.
Kingdom of fungi, structure, life, reproduction. Lichens, their diversity, features of structure and life activity. role in nature.
22.11
Plants. Building, life.
Plant kingdom. Features of the structure of tissues and organs, vital activity and reproduction of the plant organism, its integrity.
29.11
Variety and classification of plants.
6.12
Invertebrate animals. Classification, structure, life.
13.12
chordate animals. Classification, structure, life.
20.12
Man and his health.
Man. Fabrics. Organs, organ systems. Digestion. Breath. Circulation.
The structure and vital activity of tissues, organs and systems of human organs: (digestion, respiration, blood circulation)
3.01
Man. Organs, organ systems. Musculoskeletal, integumentary, excretory systems. Reproduction and development.
The structure and vital activity of tissues, organs and systems of human organs (musculoskeletal, integumentary, excretory). Reproduction and human development.
10.01
Internal environment, immunity, metabolism.
The internal environment of the human body. Immunity. Metabolism and energy conversion in the human body. Vitamins.
17.01
Structure and functions of the nervous and endocrine systems. Neurohumoral regulation of vital processes.
24.01
Man. Analyzers. GNI.
Analyzers. Sense organs. Structure and functions. Higher nervous activity. Behavior and psyche.
31.01
Health and risk factors. Human hygiene.
7.02
Superorganism systems.
Superorganismal systems: population, species.
14.02
Evolution
organic world.
Evolution of the organic world. driving forces of evolution. Ways and directions of evolution.
Results of evolution: adaptability of organisms, speciation, diversity of species.
Ch. Darwin's teaching about the driving forces of evolution. Synthetic theory of evolution. Forms natural selection, types of struggle for existence. The relationship of the driving forces of evolution. creative role natural selection in evolution.
Directions and paths of evolution: biological progress and regression, aromorphosis, idioadaptation, degeneration. Causes of biological progress and regression. Hypotheses for the origin of life on Earth. Evolution of the organic world. Complication of plants and animals in the process of evolution.
21.02
Evolution of the organic world. Human Origins.
Human Origins. Man as a species, his place in the system of the organic world. Driving forces and stages of human evolution. human races their genetic relationship. biosocial nature of man. Social and natural environment, human adaptation to it.
28.02
VII
Ecosystems and their inherent patterns.
habitats. environmental factors. The relationship of organisms.
Ecosystem and its components. Food chains. Diversity and development of ecosystems, self-regulation and change of ecosystems. Agroecosystems.
The biosphere is a global ecosystem. Teachings of V.I.Vernadsky about the biosphere and noosphere. Living matter, its functions. Evolution of the biosphere
Cycle of substances in the biosphere. Biosphere, functions of living matter. Evolution of the biosphere. Global changes in the biosphere
7.03
PRACTICAL APPLICATION OF KNOWLEDGE.
14.03
Generalization and application of knowledge about the cellular-organismal level of life organization. Comparison of the features of the structure and functioning of organisms of different kingdoms.
14.03
Generalization and application of knowledge about man and the diversity of organisms. Comparison of the features of the structure and functioning of the human body.
Solution of KIMs part 1 and part 2
21.03
Generalization and application of knowledge about the diversity of organisms. Comparison of biological objects, processes, phenomena, manifested at all levels of life organization.
Solution of KIMs part 1 and part 2
4.04
Generalization and application of knowledge about evolution and ecological patterns. Establishing the sequence of biological objects, processes, phenomena.
Solution of KIMs part 1 and part 2
11.04
Ability to work with text and graphics
Solution of KIMs part 1 and part 2
18.04
Application of biological knowledge in practical situations.
KIM solution part 2
25.04
Solving biological problems for the application of knowledge in a new situation in cytology, ecology, evolution of organisms
KIM solution part 2
2.05
Solving problems on the application of knowledge in a new situation in genetics.
KIM solution part 2
16.05
Working with 2017 variants
23.05
The video course "Get an A" includes all the topics necessary for a successful passing the exam in mathematics for 60-65 points. Completely all tasks 1-13 profile exam mathematics. Also suitable for passing the Basic USE in mathematics. If you want to pass the exam with 90-100 points, you need to solve part 1 in 30 minutes and without mistakes!
Preparation course for the exam for grades 10-11, as well as for teachers. Everything you need to solve part 1 of the exam in mathematics (the first 12 problems) and problem 13 (trigonometry). And this is more than 70 points on the Unified State Examination, and neither a hundred-point student nor a humanist can do without them.
All the necessary theory. Quick Ways solutions, traps and secrets of the exam. All relevant tasks of part 1 from the Bank of FIPI tasks have been analyzed. The course fully complies with the requirements of the USE-2018.
The course contains 5 large topics, 2.5 hours each. Each topic is given from scratch, simply and clearly.
Hundreds of exam tasks. Text problems and probability theory. Simple and easy to remember problem solving algorithms. Geometry. Theory, reference material, analysis of all types of USE tasks. Stereometry. Cunning tricks for solving, useful cheat sheets, development of spatial imagination. Trigonometry from scratch - to task 13. Understanding instead of cramming. Visual explanation complex concepts. Algebra. Roots, powers and logarithms, function and derivative. Base for solving complex problems of the 2nd part of the exam.
OPTION 1
2. Choose two correct answers out of five and write down the numbers under which they are indicated in the table. Examples of what scientific methods are illustrated by the plot of the painting by the Dutch artist J. Steen "Pulse"?
1) abstraction
2) simulation
3) experiment
4) measurement
5) observation
3. What is the function of nucleic acids in a cell?
1) are the keepers of hereditary information
2) carry out homeostasis
3) transfer hereditary information from the nucleus to the ribosome
4) participate in protein synthesis
5) are part of the cell membrane
6) perform a signaling function
4. What happens during the prophase of the first division of meiosis? |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
5. Establish a correspondence between the trait and the cell organoid for which it is characteristic. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
6. Determine the ratio of phenotypes in offspring in a monohybrid crossing of two heterozygous organisms with incomplete dominance. Write down the answer in the form of a sequence of numbers showing the ratio of the resulting phenotypes,starting with the dominant phenotype.
7. What patterns are characteristic of modification variability? |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
9. Establish a correspondence between the structure of a flower and the method of pollination of such a flower: for each position given in the first column, select the corresponding position from the second column. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
10. Mosses, unlike angiosperms, |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
12. Choose three correct answers from six and write down the numbers under which they are indicated in the table. Connective tissue of the human body |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
15. It is known that potato or tuberous nightshade, a species of herbaceous plants, is the most important food, technical and fodder crop.
Using this information, select statements from the list below that are relevant to describe these features of this organism.
Write in the table the numbers corresponding to the selected answers.
- Potato is a herbaceous plant with bare, ribbed stems and pinnate leaves.
- Potatoes are native to the coasts of Chile and Peru.
- Europeans did not know the potato until 1565, before visiting South America the Spaniards.
- Until the end of the 18th century, potatoes were cultivated as an ornamental plant.
- Starch, molasses and alcohol are obtained from potato tubers.
- Potatoes are used for fattening farm animals.
16. Establish a correspondence between the example and the factor of anthropogenesis for which it is characteristic. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
17 . In agrocenosis, in contrast to the natural ecosystem, |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
18. Set the correspondence between the example and the group environmental factors which he illustrates. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
19. Establish the sequence of evolutionary processes of formation of the main groups of animals that took place on Earth, in chronological order. Write down the corresponding sequence of numbers in the table
20 . Insert the missing terms from the proposed list into the text “The similarity of mushrooms with plants and animals”, using digital symbols for this. Write down the numbers of the selected answers in the text, and then enter the resulting sequence of numbers (in the text) into the table below.
SIMILARITY OF MUSHROOMS WITH PLANTS AND ANIMALS
Mushrooms combine features of both plants and animals. Like plants, fungi are immobile and constantly growing. Outside, their cells, like plant cells, are covered with ___________ (A). Inside the cell, they do not have green ___________ (B). Mushrooms are similar to animals in that they do not store ___________ (B) in their cells and they feed on ready-made organic substances. The cell wall of fungi contains ___________(D).
LIST OF TERMS:
1) plasma membrane 2) cell wall 3) plastids 4) Golgi complex
5) mitochondria 6) starch 7) glycogen 8) chitin
21. P Using the "Nutritional value of some fish" table and knowledge of biology, choose the correct statements
1) Salmon contains the highest proportion of proteins compared to other fish.
2) Sprat contains the highest proportion of fats compared to other fish.
4) Vobla is the lowest calorie fish.
5) All of these fish are representatives of the herring order.
Part 2
22. Why is it not recommended to store wet seeds in a granary? What happens to them?
23. What are the formations on the roots of the depicted plant? What type of relationship between organisms does the picture illustrate? Explain the significance of these relationships for both organisms.
24. Find three errors in the given text. Indicate the numbers of sentences in which errors were made, correct them.
1. Fungi and bacteria are classified as prokaryotes. 2. There is a wide variety among fungi: yeasts, molds, cap mushrooms, etc. 3. A common feature of multicellular fungi is the formation of a vegetative body from thin branching filaments that form a mycelium. 4. A fungal cell has a cell wall consisting of chitin and membrane organelles. 5. The reserve nutrient is glycogen. 6. Mushrooms have an autotrophic type of nutrition. 7. Mushroom growth stops after spores mature.
25. What are the functions in the human body nervous system? List at least three functions. Explain the answer.
26. Flounder is a bottom fish, adapted to life in the seas, merges with the background of the seabed. Name the type of coloration and explain its meaning, as well as the relative nature of fitness.
27. The chromosome set of potato somatic cells is 48. Determine the chromosome set and the number of DNA molecules in cells during meiosis in meiosis prophase I and meiosis metaphase II. Explain all your results.
28. In homozygous sheep, the gray gene causes embryonic death. In the first crossing of sheep with gray wool, horned, part of the offspring turned out with black wool, hornless. In the second crossing between sheep with a gray coat, horned (homozygous), offspring with a gray coat, horned and with a black coat, horned in a ratio of 2: 1 were obtained. The genes are not linked. Make a scheme for solving the problem. Determine the genotypes of parental individuals, genotypes and phenotypes of possible offspring in crosses. Explain the phenotypic splitting of offspring in two crosses.
OPTION 2
- Review the diagram. Write in the diagram the missing term, indicated by a question mark.
- Choose two correct answers out of five and write down the numbers under which they are indicated in the table. The banding method is used for
1) determining the timing and ways of bird migration
2) studying the mechanisms of flight of birds at different heights
3) determining the characteristics of the behavior of poultry
4) assessment of the damage caused to humans by birds
5) determining the life span of birds
3. Diploid set of chromosomes |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
4. Prokaryotic cells are different from eukaryotic cells |
||||||||||||||||||
|
5. Establish a correspondence between the structure of the organoid and its appearance. |
|
6. Determine the ratio of phenotypes in the offspring when crossing females and males with AaBb genotypes, given that the genes are not linked to each other and complete dominance is observed. Write down the answer in the form of a sequence of numbers showing the ratio of the resulting phenotypes,in descending order.
7. The causes of combinative variability include |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
8. Establish a correspondence between the characteristic of variability and its type. |
|||||||||||||||||||
15. It is known that the common mole is a soil mammal that feeds on animal food. Using this information, select three statements from the list below that relate to the description of these features of this animal. Write in the table the numbers corresponding to the selected answers. 1) The body length of the animals is 18–26.5 cm, and the weight is 170–319 g. 2) Adult animals are quarrelsome with each other, attack relatives who have fallen on their site and can bite them to death. 3) The offspring of moles are born blind, naked and helpless. At this time, the female feeds him with milk. 4) The nesting chamber is located at a depth of 1.5–2 m. 5) Along the river valleys, the mole penetrates north to the middle taiga, and south to the typical steppes. 6) The mole feeds on earthworms, eats slugs, insects and their larvae in smaller quantities. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
17. Choose three correct answers from six and write down the numbers under which they are indicated in the table. In a mixed forest ecosystem, symbiotic relationships are established between | psilophytes |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Multicellular algae |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Angiosperms |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ferns |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
20. Insert the missing terms from the proposed list into the text "Life activity of a plant" using numerals for this. Write down the numbers of the selected answers in the text, and then enter the resulting sequence of numbers (in the text) into the table below.
PLANT LIFE
The plant receives water in the form of a soil solution with the help of ___________ (A) roots. The terrestrial parts of the plant, mainly ___________ (B), on the contrary, through special cells - ___________ (C) evaporate a significant amount of water. In this case, water is used not only for evaporation, but also as a starting material for the formation of organic substances during the process ___________ (D) .
LIST OF TERMS:
1) breath 2) root cap 3) root hair 4) leaf
5) shoot 6) stem 7) stomata 8) photosynthesis
21. Using the table "Acidity of juices and secrets in the human digestive tract" and knowledge of the biology course, select the correct statements:
2) With heartburn, the pH of the esophagus drops sharply.
3) In an empty (fasting) stomach, the most alkaline environment.
4) When fasting, there is a danger of developing a duodenal ulcer.
5) In the acidic environment of the stomach, carbohydrates are better broken down.
Part 2.
22. It is known that at high temperatures environment the skin of the face turns red, and at low turns pale. Explain why this is happening.
23. Name the organism shown in the figure and the kingdom to which it belongs. What is indicated by the numbers 1, 2? What is the role of these organisms in the ecosystem?
24. Find three errors in the given text. Indicate the numbers of the proposals in which they are made, correct them.
1. G. Mendel is rightfully considered the founder of genetics. 2. He found that during monohybrid crossing, splitting of traits occurs in a ratio of 3: 1. 3. During dihybrid crossing, splitting of traits occurs in the second generation in a ratio of 1: 2: 1. 4. Such splitting occurs if the genes are located in non-homologous chromosomes. 5. T. Morgan found that if the genes are located on the same chromosome, then the traits are inherited exclusively together, that is, linked. 6. Such genes form a linkage group. 7. The number of linkage groups is equal to the diploid set of chromosomes.
25. What is the role of mitochondria in metabolism? Which tissue - muscle or connective - contains more mitochondria? Explain why.
26. What is expressed negative influence human activity on vegetable world biosphere? Give at least four examples and explain their impact.
27. The karyotype of one of the fish species is 56 chromosomes. Determine the number of chromosomes during spermatogenesis in the cells of the growth zone and in the cells of the maturation zone at the end of the first division. Explain what processes take place in these zones.
28. In humans, deafness is an autosomal, recessive trait; color blindness is a recessive sex-linked trait (Xd). A healthy woman according to these two signs married a man suffering from deafness and color blindness. They had a daughter with good hearing and color blind and a son who was deaf and color blind. Make a scheme for solving the problem. Determine the genotypes of the parents, all possible genotypes and phenotypes of the children. Determine the probability of the birth of children suffering from both anomalies. What gender will they be? Specify their genotypes.
