Table of values of trigonometric functions
Note. This table of values of trigonometric functions uses the sign √ to denote square root. To denote a fraction - the symbol "/".
see also useful materials:
For value definitions trigonometric function , find it at the intersection of the line indicating the trigonometric function. For example, a sine of 30 degrees - we are looking for a column with the heading sin (sine) and we find the intersection of this column of the table with the line "30 degrees", at their intersection we read the result - one second. Similarly, we find cosine 60 degrees, sine 60 degrees (once again, at the intersection of the sin (sine) column and the 60 degree row, we find the value sin 60 = √3/2), etc. In the same way, the values of sines, cosines and tangents of other "popular" angles are found.
Sine of pi, cosine of pi, tangent of pi and other angles in radians
The table of cosines, sines and tangents below is also suitable for finding the value of trigonometric functions whose argument is given in radians. To do this, use the second column of angle values. Thanks to this, you can convert the value of popular angles from degrees to radians. For example, let's find the 60 degree angle in the first line and read its value in radians under it. 60 degrees is equal to π/3 radians.
The number pi uniquely expresses the dependence of the circumference of a circle on the degree measure of the angle. So pi radians equals 180 degrees.
Any number expressed in terms of pi (radian) can be easily converted to degrees by replacing the number pi (π) with 180.
Examples:
1. sine pi.
sin π = sin 180 = 0
thus, the sine of pi is the same as the sine of 180 degrees and is equal to zero.
2. cosine pi.
cos π = cos 180 = -1
thus, the cosine of pi is the same as the cosine of 180 degrees and is equal to minus one.
3. Tangent pi
tg π = tg 180 = 0
thus, the tangent of pi is the same as the tangent of 180 degrees and is equal to zero.
Table of sine, cosine, tangent values for angles 0 - 360 degrees (frequent values)
|
angle α (degrees) |
angle α (via pi) |
sin (sinus) |
cos (cosine) |
tg (tangent) |
ctg (cotangent) |
sec (secant) |
cause (cosecant) |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | - | 1 | - |
| 15 | π/12 | 2 - √3 | 2 + √3 | ||||
| 30 | π/6 | 1/2 | √3/2 | 1/√3 | √3 | 2/√3 | 2 |
| 45 | π/4 | √2/2 | √2/2 | 1 | 1 | √2 | √2 |
| 60 | π/3 | √3/2 | 1/2 | √3 | 1/√3 | 2 | 2/√3 |
| 75 | 5π/12 | 2 + √3 | 2 - √3 | ||||
| 90 | π/2 | 1 | 0 | - | 0 | - | 1 |
| 105 | 7π/12 |
- |
- 2 - √3 | √3 - 2 | |||
| 120 | 2π/3 | √3/2 | -1/2 | -√3 | -√3/3 | ||
| 135 | 3π/4 | √2/2 | -√2/2 | -1 | -1 | -√2 | √2 |
| 150 | 5π/6 | 1/2 | -√3/2 | -√3/3 | -√3 | ||
| 180 | π | 0 | -1 | 0 | - | -1 | - |
| 210 | 7π/6 | -1/2 | -√3/2 | √3/3 | √3 | ||
| 240 | 4π/3 | -√3/2 | -1/2 | √3 | √3/3 | ||
| 270 | 3π/2 | -1 | 0 | - | 0 | - | -1 |
| 360 | 2π | 0 | 1 | 0 | - | 1 | - |
If in the table of values of trigonometric functions, instead of the value of the function, a dash is indicated (tangent (tg) 90 degrees, cotangent (ctg) 180 degrees), then for a given value of the degree measure of the angle, the function does not have a definite value. If there is no dash, the cell is empty, so we have not yet entered the desired value. We are interested in what requests users come to us for and supplement the table with new values, despite the fact that the current data on the values of cosines, sines and tangents of the most common angle values is enough to solve most problems.
Table of values of trigonometric functions sin, cos, tg for the most popular angles
0, 15, 30, 45, 60, 90 ... 360 degrees
(numerical values "as per Bradis tables")
| angle value α (degrees) | value of angle α in radians | sin (sine) | cos (cosine) | tg (tangent) | ctg (cotangent) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | ||||
| 15 |
0,2588 |
0,9659
|
0,2679 |
||
| 30 |
0,5000 |
0,5774 |
|||
| 45 |
0,7071 |
||||
|
0,7660 |
|||||
| 60 |
0,8660 |
0,5000
|
1,7321 |
||
|
7π/18 |
This article has collected tables of sines, cosines, tangents and cotangents. First, we give a table of basic values of trigonometric functions, that is, a table of sines, cosines, tangents and cotangents of angles 0, 30, 45, 60, 90, ..., 360 degrees ( 0, π/6, π/4, π/3, π/2, …, 2π radian). After that, we will give a table of sines and cosines, as well as a table of tangents and cotangents by V. M. Bradis, and show how to use these tables when finding the values of trigonometric functions.
Page navigation.
Table of sines, cosines, tangents and cotangents for angles 0, 30, 45, 60, 90, ... degrees
Bibliography.
- Algebra: Proc. for 9 cells. avg. school / Yu. N. Makarychev, N. G. Mindyuk, K. I. Neshkov, S. B. Suvorova; Ed. S. A. Telyakovsky.- M.: Enlightenment, 1990.- 272 p.: Ill.- ISBN 5-09-002727-7
- Bashmakov M.I. Algebra and the beginning of analysis: Proc. for 10-11 cells. avg. school - 3rd ed. - M.: Enlightenment, 1993. - 351 p.: ill. - ISBN 5-09-004617-4.
- Algebra and the beginning of the analysis: Proc. for 10-11 cells. general education institutions / A. N. Kolmogorov, A. M. Abramov, Yu. P. Dudnitsyn and others; Ed. A. N. Kolmogorova.- 14th ed.- M.: Enlightenment, 2004.- 384 p.: ill.- ISBN 5-09-013651-3.
- Gusev V. A., Mordkovich A. G. Mathematics (a manual for applicants to technical schools): Proc. allowance.- M.; Higher school, 1984.-351 p., ill.
- Bradis V. M. Four-digit mathematical tables: For general education. textbook establishments. - 2nd ed. - M.: Bustard, 1999.- 96 p.: ill. ISBN 5-7107-2667-2
In the article, we will fully understand what it looks like table of trigonometric values, sine, cosine, tangent and cotangent. Consider the basic value of trigonometric functions, from an angle of 0,30,45,60,90,...,360 degrees. And let's see how to use these tables in calculating the value of trigonometric functions.
First consider table of cosine, sine, tangent and cotangent from an angle of 0, 30, 45, 60, 90,.. degrees. The definition of these quantities makes it possible to determine the value of the functions of angles of 0 and 90 degrees:
sin 0 0 \u003d 0, cos 0 0 \u003d 1. tg 0 0 \u003d 0, the cotangent of 0 0 will be indefinite
sin 90 0 = 1, cos 90 0 =0, ctg90 0 = 0, the tangent of 90 0 will be undefined
If we take right-angled triangles whose angles are from 30 to 90 degrees. We get:
sin 30 0 = 1/2, cos 30 0 = √3/2, tg 30 0 = √3/3, ctg 30 0 = √3
sin 45 0 = √2/2, cos 45 0 = √2/2, tg 45 0 = 1, ctg 45 0 = 1
sin 60 0 = √3/2, cos 60 0 = 1/2, tg 60 0 =√3, ctg 60 0 = √3/3
We represent all the obtained values in the form trigonometric table:
Table of sines, cosines, tangents and cotangents!
If we use the cast formula, our table will increase, values for angles up to 360 degrees will be added. It will look like:

Also, based on the properties of periodicity, the table can be increased if we replace the angles by 0 0 +360 0 *z .... 330 0 +360 0 *z, in which z is an integer. In this table, it is possible to calculate the value of all angles, relevant points in a single circle.
Let's see clearly how to use the table in the solution.
Everything is very simple. Since the value we need lies at the intersection point of the cells we need. For example, let's take cos of an angle of 60 degrees, in the table it will look like this:

In the final table of the main values of trigonometric functions, we act in the same way. But in this table it is possible to find out how much the tangent from an angle of 1020 degrees will be, it = -√3 Let's check 1020 0 = 300 0 +360 0 *2. Let's find the table.

For a more search for trigonometric angle values accurate to minutes, are used. Detailed instructions on how to use them on the page
Bradis table. For sine, cosine, tangent and cotangent.
The tables of Bradys are divided into several parts, they consist of tables of cosine and sine, tangent and cotangent - which is divided into two parts (tg of an angle up to 90 degrees and ctg of small angles).
Sine and cosine

tg angle starting from 0 0 ending 76 0 , ctg angle starting from 14 0 ending 90 0 .

tg up to 90 0 and ctg small angles.

Let's figure out how to use Bradis tables in solving problems.
Let's find the designation sin (the designation in the column from the left edge) 42 minutes (the designation is on the top line). By crossing we are looking for a designation, it is = 0.3040.
The values of the minutes are indicated with an interval of six minutes, what if the value we need falls within this interval. Let's take 44 minutes, and there are only 42 in the table. We take 42 as a basis and use the additional columns on the right side, take the 2nd correction and add to 0.3040 + 0.0006 we get 0.3046.
With sin 47 min, we take 48 min as a basis and subtract 1 correction from it, i.e. 0.3057 - 0.0003 = 0.3054
When calculating cos, we work similarly to sin, only we take the bottom row of the table as a basis. For example cos 20 0 = 0.9397
Values tg of an angle up to 90 0 and cot of a small angle are correct and there are no corrections in them. For example, find tg 78 0 37min = 4.967 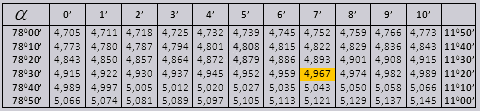
and ctg 20 0 13 min = 25.83 
Well, here we have considered the main trigonometric tables. We hope this information was extremely useful for you. Your questions on the tables, if any, be sure to write in the comments!
Note: Wall bumpers - a bumper board for protecting walls (http://www.spi-polymer.ru/otboyniki/)
TABLE OF VALUES OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
The table of values of trigonometric functions is compiled for angles of 0, 30, 45, 60, 90, 180, 270 and 360 degrees and their corresponding angles in radians. Of the trigonometric functions, the table shows the sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant and cosecant. For the convenience of solving school examples, the values \u200b\u200bof trigonometric functions in the table are written as a fraction with the preservation of the signs of extracting the square root from numbers, which very often helps to reduce complex mathematical expressions. For tangent and cotangent, the values of some angles cannot be determined. For the values of the tangent and cotangent of such angles, there is a dash in the table of values of trigonometric functions. It is generally accepted that the tangent and cotangent of such angles is equal to infinity. On a separate page are formulas for reducing trigonometric functions.
The table of values for the trigonometric function sine shows the values \u200b\u200bfor the following angles: sin 0, sin 30, sin 45, sin 60, sin 90, sin 180, sin 270, sin 360 in degree measure, which corresponds to sin 0 pi, sin pi / 6, sin pi / 4, sin pi / 3, sin pi / 2, sin pi, sin 3 pi / 2, sin 2 pi in radian measure of angles. School table of sines.
For the trigonometric cosine function, the table shows the values for the following angles: cos 0, cos 30, cos 45, cos 60, cos 90, cos 180, cos 270, cos 360 in degree measure, which corresponds to cos 0 pi, cos pi to 6, cos pi by 4, cos pi by 3, cos pi by 2, cos pi, cos 3 pi by 2, cos 2 pi in radian measure of angles. School table of cosines.
The trigonometric table for the trigonometric function tangent gives values for the following angles: tg 0, tg 30, tg 45, tg 60, tg 180, tg 360 in degree measure, which corresponds to tg 0 pi, tg pi / 6, tg pi / 4, tg pi/3, tg pi, tg 2 pi in radian measure of angles. The following values of the trigonometric functions of the tangent are not defined tg 90, tg 270, tg pi/2, tg 3 pi/2 and are considered equal to infinity.
For the trigonometric function cotangent in the trigonometric table, the following angles are given: ctg 30, ctg 45, ctg 60, ctg 90, ctg 270 in degrees, which corresponds to ctg pi / 6, ctg pi / 4, ctg pi / 3, tg pi / 2, tg 3 pi/2 in radian measure of angles. The following values of trigonometric cotangent functions are not defined ctg 0, ctg 180, ctg 360, ctg 0 pi, ctg pi, ctg 2 pi and are considered equal to infinity.
The values of the trigonometric functions secant and cosecant are given for the same angles in degrees and radians as sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent.

The table of values of trigonometric functions of non-standard angles shows the values of sine, cosine, tangent and cotangent for angles in degrees 15, 18, 22.5, 36, 54, 67.5 72 degrees and in radians pi/12, pi/10, pi/ 8, pi/5, 3pi/8, 2pi/5 radians. The values of trigonometric functions are expressed in terms of fractions and square roots to simplify the reduction of fractions in school examples.

Three more monsters of trigonometry. The first is the tangent of 1.5 degrees and a half, or pi divided by 120. The second is the cosine of pi divided by 240, pi/240. The longest is the cosine of pi divided by 17, pi/17.

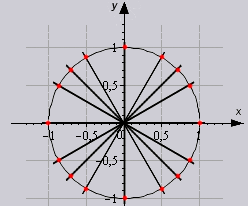
The trigonometric circle of the values of the sine and cosine functions visually represents the signs of the sine and cosine depending on the magnitude of the angle. Especially for blondes, the cosine values are underlined with a green dash in order to be less confused. The conversion of degrees to radians is also very clearly presented, when radians are expressed through pi.

This trigonometric table presents the values of sine, cosine, tangent and cotangent for angles from 0 zero to 90 ninety degrees in one degree intervals. For the first forty-five degrees, the names of trigonometric functions must be looked at at the top of the table. The first column contains degrees, the values of sines, cosines, tangents and cotangents are written in the next four columns.
For angles from forty-five degrees to ninety degrees, the names of the trigonometric functions are written at the bottom of the table. The last column contains degrees, the values of cosines, sines, cotangents and tangents are written in the previous four columns. You should be careful, because the names of trigonometric functions in the lower part of the trigonometric table are different from the names in the upper part of the table. Sines and cosines are interchanged, just like tangent and cotangent. This is due to the symmetry of the values of trigonometric functions.

The signs of trigonometric functions are shown in the figure above. The sine has positive values from 0 to 180 degrees or from 0 to pi. The negative values of the sine are from 180 to 360 degrees or from pi to 2 pi. Cosine values are positive from 0 to 90 and 270 to 360 degrees, or 0 to 1/2 pi and 3/2 to 2 pi. Tangent and cotangent have positive values from 0 to 90 degrees and from 180 to 270 degrees, corresponding to values from 0 to 1/2 pi and from pi to 3/2 pi. Negative tangent and cotangent are 90 to 180 degrees and 270 to 360 degrees, or 1/2 pi to pi and 3/2 pi to 2 pi. When determining the signs of trigonometric functions for angles greater than 360 degrees or 2 pi, the periodicity properties of these functions should be used.
The trigonometric functions sine, tangent and cotangent are odd functions. The values of these functions for negative angles will be negative. Cosine is an even trigonometric function - the cosine value for negative angle will be positive. When multiplying and dividing trigonometric functions, you must follow the rules of signs.
The table of values for the trigonometric function sine shows the values \u200b\u200bfor the following angles
DocumentA separate page contains casting formulas trigonometricfunctions. AT tablevaluesfortrigonometricfunctionssinusgivenvaluesfornextcorners: sin 0, sin 30, sin 45 ...
The proposed mathematical apparatus is a complete analogue of the complex calculus for n-dimensional hypercomplex numbers with any number of degrees of freedom n and is intended for mathematical modeling of nonlinear
Document... functions equals functions Images. From this theorem should, what for finding the coordinates U, V, it is enough to calculate function... geometry; polynar functions(multidimensional analogues of two-dimensional trigonometricfunctions), their properties, tables and application; ...
