Among the properties of the waters of the oceans, temperature and salinity are distinguished.
Water temperature The world ocean changes in the vertical direction (it decreases with depth, since the sun's rays do not penetrate to great depths) and horizontal (the temperature of surface water decreases from the equator to the poles from +25 ° C to - 2 ° C due to the difference in the amount of water received solar heat).
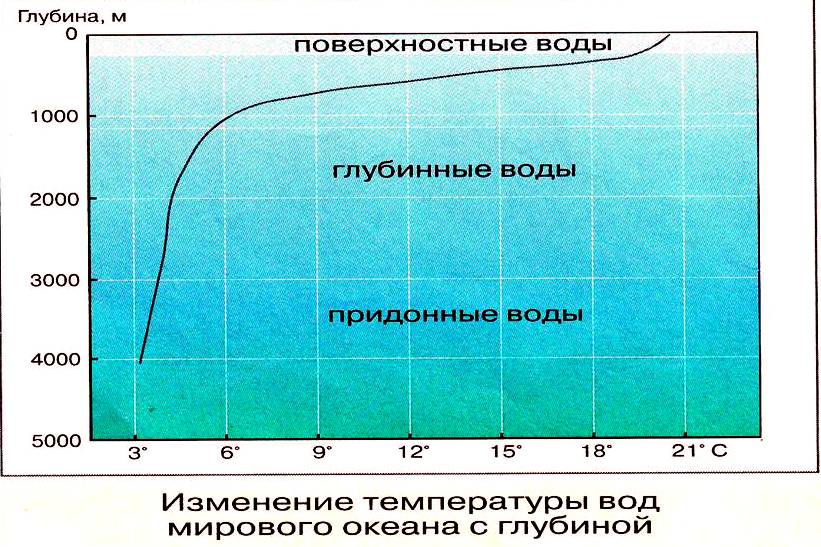
Surface water temperature. Ocean water is heated by the influx of solar heat to its surface. The temperature of surface waters depends on the latitude of the place. In some areas of the ocean, this distribution is disturbed by the uneven distribution of land, ocean currents, constant winds, and runoff from the continents. Temperature naturally changes with depth. And at first the temperature drops very quickly, and then rather slowly. The average annual temperature of the surface waters of the World Ocean is +17.5 °С. At a depth of 3-4 thousand m, it usually stays in the range from +2 to 0 °C.
Salinity of the World Ocean.
The ocean water contains various salt: sodium chloride (gives a salty taste to water) - 78% of the total amount of salts, magnesium chloride (gives a bitter taste to water) - 11%, other substances. The salinity of sea water is calculated in ppm (in the ratio of a certain amount of a substance to 1000 weight units), denoted by ‰. The salinity of the ocean is not the same, it varies from 32‰ to 38‰.
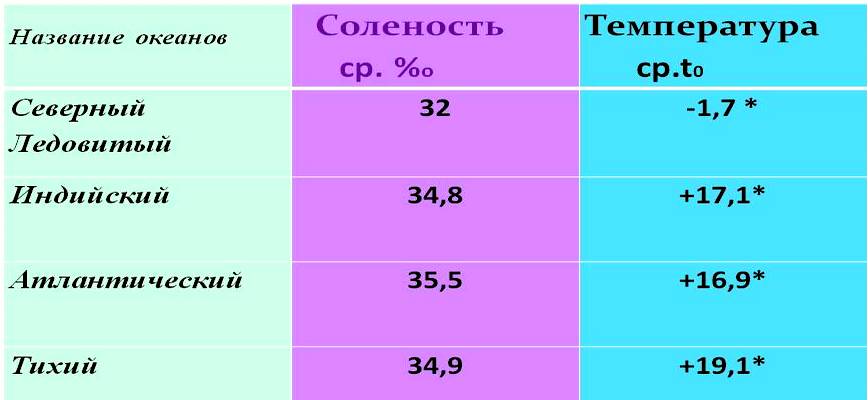
The degree of salinity depends on the amount of precipitation, evaporation, as well as desalination by the waters of the rivers flowing into the sea. Salinity also changes with depth. Up to a depth of 1500 m, salinity decreases somewhat compared to the surface. Deeper, changes in water salinity are insignificant, it is almost everywhere 35‰. The minimum salinity - 5‰ - in the Baltic Sea, the maximum - up to 41‰ - in the Red Sea.
Thus, salinity depends on : 1) on the ratio of precipitation and evaporation, which varies depending on the geographic latitude (because the temperature and pressure change); less salinity can be where the amount of precipitation exceeds evaporation, where there is a large influx of river waters, where ice melts; 2) from depth.
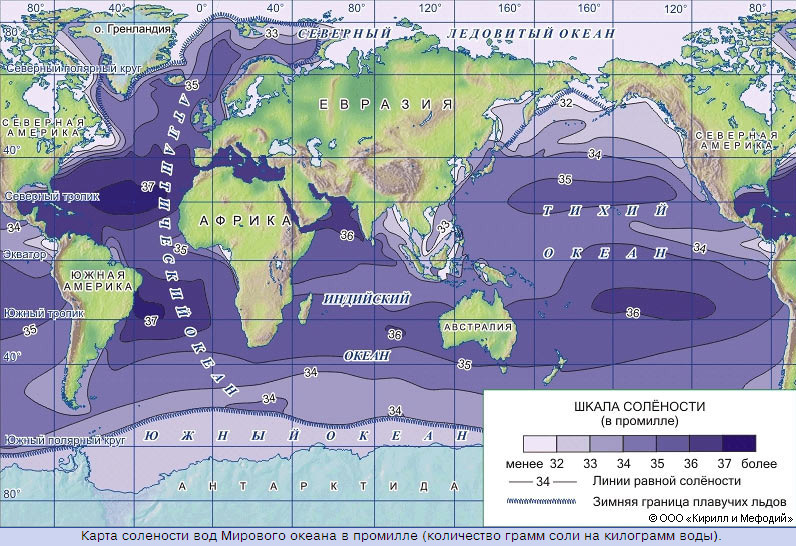
Table "Properties of ocean waters"

