The water in the sea and in the river is very different. First of all, it has a salty taste in the sea or ocean. This is due to various factors, and what exactly affects the average salinity of the world's oceans will be discussed further.
salinity sign
Scientists have come up with a special designation for salinity. It is called ppm, and is very similar to%, but differs by an additional zero behind - ‰. Ppm shows what the volume of a substance dissolved in one liter of water is equal to. If we have a component and its quantity is 2 grams per liter of water, then we have a value of 2 ‰.
Why is water bitter?
Have you noticed how the water in the sea tastes?
It's not just salty, it's also bitter. This is due to its heterogeneity. It contains 44 different natural elements. But the main ones are salts. We are used to cooking - it gives an ordinary flavor, as in any food. But another, magnesium salt, is very bitter, and if there is more of it, then the water will seem nasty.
There is so much salt in the ocean that if you dry it all and sprinkle it on land, you get a layer at least 150 meters high.
Factors affecting the level of taste in ocean water
Consider what determines the average salinity of the world's oceans:
- Evaporation. The more the water leaves its location, the more solid particles remain in the ocean. Salts do not evaporate.
- Are there glaciers in the ocean, and how intense is their melting. Cold natural conditions can affect the level of salts in the water in different ways. If the process of ice formation occurs, then all the fresh water goes into the snow, and the minerals remain, increasing their concentration. Conversely, the more glaciers melt, the more they dilute the water.
- Rainfall per year. The more fresh rain waters the ocean, the less salinity.
- Waste water quantity. All rivers are freshwater, and naturally, the more rivers flow into the global water area, the lower the concentration of substances.
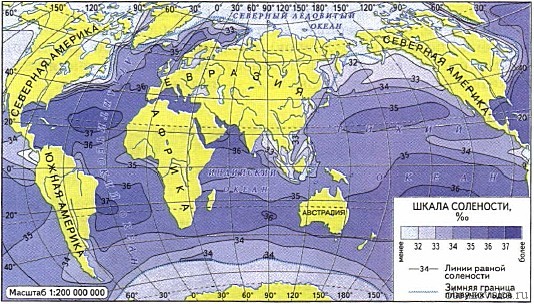
Rice. 1. Map of the oceans and the value of salinity depending on latitude
Places with the lowest and highest ppm
In the world's oceans, the value of ppm is very different. The highest results are noticeable in the North Atlantic Ocean (between 20° and 30°) and reach a level of 37 ‰. And if you measure the water in the Gulf of Panama, then here the indicator will be 28‰. The lowest value part of the ocean is between two continents and receives so much tropical rainfall that the concentration of solids is low. In the Atlantic, it's the other way around. Latitudes 20°-30° are located close to the equator, which means that there is little precipitation, and evaporation is large.
TOP 1 articlewho read along with this
The average salinity value throughout the water area is 35‰.
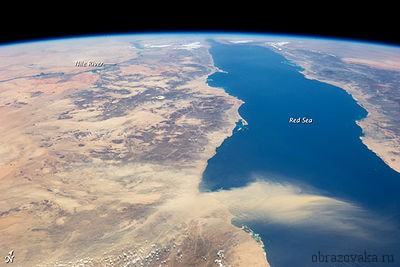
Rice. 2. Red Sea: view from space
The sea with the highest ppm value is the Red Sea (42‰). It has a unique geographical location because no rivers flow into it, and the arid climate results in abundant evaporation.
The Baltic Sea is the freshest. The ppm indicator is 1 ‰. The location in the North of Europe suggests that, firstly, most European rivers flow into it, and secondly, there is a very rainy climate here, and there are few hot days.
The salinity of the waters in the ocean is also affected by currents. The largest is the Gulf Stream. It carries water with a value of 35‰ from the south to the Arctic Ocean, where the salinity is only 10-11‰. And another current - Labrador has the opposite effect. It carries the fresh waters of the Arctic to the hot climate of Central America.
