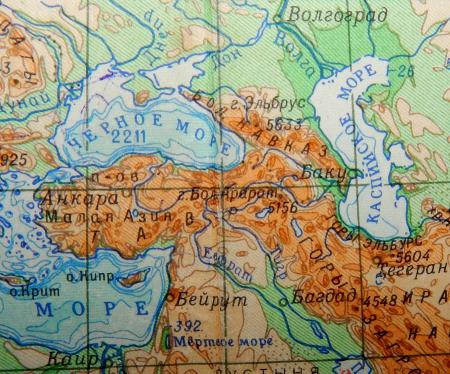
The Black Sea is inland, its water area is surrounded by land on all sides, only narrow straits lead to the Mediterranean Sea. This entire area belongs to the Atlantic Ocean basin. The salinity of the Black Sea is lower than that of the Mediterranean and Red. The runoff of large rivers desalinates the water area, but its mystery is the formation of a layer of heavier salty water at a depth, the accumulation of dissolved hydrogen sulfide. All this does not interfere with beach and cruise vacations, shipping and fishing. After all, the surface layers are devoid of H 2 S and are well warmed up by the sun.
Cradle of ancient civilizations
The Black Sea is shaped like an oval, elongated in the latitudinal direction. This basin is almost closed, separated by large land masses from other parts of the World Ocean (MO). In the northeast, the Crimean peninsula deeply cuts into the water area, its northeast separates the Black and Azov Seas. The basin is located in the southwestern part of the Eurasian continent. On its surface, from the northeast to the southwest, a border was drawn between two parts of the world - Asia and Europe.
Since ancient times, the life of millions of people has been connected with the waters of the Black and Mediterranean Seas, legends about giants and monsters were born here, the greatest discoveries were made. Suffice it to recall that legends about Scylla and Kharbida, the voyage of the Argonauts led by Jason for the Golden Fleece to Colchis are connected with the straits and the peninsulas and islands surrounding them. Even in ancient times, Greek sailors and merchants highly valued the fish riches of this area, created prosperous colony cities on the shores, the remains of which can be seen on the Crimean peninsula. It is difficult to say what the salinity of the Black Sea was in ppm several thousand years ago. This indicator was introduced relatively recently, when a consistent and purposeful study of hydrological features began.
The most important geographical features affecting the salinity of the sea
Through the narrow straits of the Bosporus and the Dardanelles, the Black Sea basin is connected in series with the Sea of Marmara and the Aegean, leading to the Mediterranean, which, in turn, communicates with the Atlantic Ocean through the Strait of Gibraltar. All of the listed parts of the Moscow Region are navigable and are located in the eastern part of the Atlantic. Physical and geographical features that significantly or moderately affect the salinity of the Black Sea:
- location in the northern temperate and subtropical climatic zones;
- a large catchment area that determines the flow of fresh water from rivers;
- weak connection with the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea;
- average depth 1240 m, maximum depth 2210 m;
- absence of large tidal waves and low tides.

river runoff
Many European rivers carry their waters from west to east and from north to south. The largest natural channel of the Old World - r. Danube - flows through 10 countries and brings huge fresh masses to the Black Sea. Other large and medium rivers of this basin: Dnieper, Don, Kuban, Bug, Rioni, Dniester.
Fresh river water mixes little with deeper and denser layers, so a significant part of the fresh runoff evaporates from the sea surface. But its volume is so great that it raises the level of the Black Sea water by 5 m relative to the average marks of the Atlantic Ocean. The temperature and salinity of the Black Sea, on the contrary, is lower than in the neighboring parts of the Mediterranean Sea. This feature led to the birth of a current directed to the southwest, towards the Bosporus.

Water mineralization
Studying the salinity of the water of the Black Sea and other parts of the MO, researchers measure not only the total content of dissolved substances in different layers and parts of the water area, but also determine the elemental composition. In addition to H 2 O molecules, sea water contains gaseous substances, mineral and organic compounds in the form of ions, molecules and other particles. The main components of salts in the Black Sea: carbonates, sulfates, nitrates and chlorides of calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium. The presence of these dissolved substances is associated with the composition of rocks on land and the seabed. The salinity of the Black Sea is affected by various compounds that come with surface and underground runoff, precipitation. Chemical interactions occur between substances, which also affects the performance.
Water is enriched not only with salts from the composition of dissolved minerals and rocks, there is also organic matter. A significant part of the surface of the Northern Black Sea region is composed of limestone, hence the high content of calcium, magnesium and sodium salts in the water. Basalt rocks, when dissolved, increase the amount of silicon and iron. Substances contained in water increase its overall mineralization. It changes noticeably over the seasons, from the surface to the depths, from north to south, so reference books, textbooks and atlases may contain different indicators characterizing the salinity of the Black Sea. Most often, average values are given based on long-term data.
What is salinity?
Almost the entire periodic table is present in sea water. But salinity is only the amount of dissolved substances in grams, which are obtained in solid form after evaporating 1 kg of sea water. For convenience, this indicator is expressed as a percentage and ppm.
To facilitate calculations, the content of all halogens is equated to the equivalent amount of molecular chlorine. There are other features, for example, heating is accompanied by the removal of dissolved gaseous substances. When the precipitate is calcined, the organic matter decomposes.
Salinity of the Black Sea in percent
To characterize the indicator under study as a percentage, one must remember the name of the content of a solute in 100 g of a solution. This is a mass fraction, its percentage value can be found by dividing the mass of the solute by the mass of the solution and multiplying by 100%. Suppose, when evaporating 1000 ml of water, a precipitate was obtained, the mass of which is 17 g. The mass fraction (%) of dissolved substances is 1.7%.

Salinity of the Black Sea in ppm
The experimental determination of the mass of dissolved salts in terms of 1 kg of Black Sea water gives different indicators - from 8 to 22 g. To determine the salinity in ppm, let's take the value mentioned more often than others in the literature on the Black Sea - 17 g. A percentage is one hundredth of a , and ppm is one thousandth. Divide 17 g by 1000 g and multiply by 1000 (‰). Thus, we get that the average salinity of the Black Sea is 17‰ (ppm). For comparison, we present the average values for the World Ocean - 35‰. The salinity of the Red Sea is 42 ‰, the Kara Sea is 8 ‰. It turns out that the content of dissolved substances in the Black Sea water is almost 2.5 times lower than in the Red Sea.
A simple experiment to determine salinity
There is a way to find out for yourself what mass of substances is contained in sea or fresh water. The experiment is simple, interesting, but for its implementation you will need heat-resistant dishes, a heater and a chemical balance. It should also be taken into account that the density of the saline solution is higher. Therefore, the mass of 1000 ml of sea water is greater than 1000 g. Hence, without taking into account density, the calculations will be approximate.

To find out what the salinity of the Black Sea is, 100-200 ml of sea water will be required. The experience is as follows:
- Measure the volume and heat the selected liquid in an evaporating cup to a boil.
- When all the water has evaporated, a white coating will remain at the bottom of the dish.
- It is necessary to collect the sediment on a piece of paper and weigh it on the scales.
- The result obtained is the total mass of all dissolved substances in the sample.
How indicators of salinity and water temperature change
The salinity of the Black Sea water in ancient times, as well as in subsequent centuries, was subject to fluctuations under the influence of climatic, meteorological factors, the water regime in the coastal regions and the economic activities of the population. The mineralization of water largely depends on the total runoff of large and small rivers. During dry periods, the channels become shallow, less fresh water enters the sea, and the salt content rises.

The main patterns that have developed to date:
- salinity of the surface layers of the Black Sea is 15-18‰, deep - 22.5-22.6‰;
- plumes of low salinity water spread from the northwest along the coast to the south, from the southeast - along the coast of the Caucasus in a northerly direction;
- under the influence of river runoff, the salinity of the surface layer of the sea in the northwest can decrease to 10‰;
- salinity in the Bosphorus region is increased by the incoming water of the Sea of Marmara;
- the surface temperature in summer is 27-28 ° C near the Black Sea coasts, in the central part of the water area - up to 22 ° C;
- the maximum salinity of surface waters - 18.3‰ - is located in the east of the central part of the water area, south of Crimea.
- the maximum salinity at a depth of 100 m is located south of the Kerch Strait - over 20.6‰;
- from the surface to 150-200 m the temperature decreases and reaches about 9 °C;
- at a depth of 150 m there is practically no oxygen, hydrogen sulfide appears;
- in winter, the surface of the Black Sea is very cold, in the northern part it can drop to minus levels, but more often it is protected at a level of 8-9 ° С.

During freezing, fluctuations in hydrological parameters are observed. Some parts of the water area are partially covered with ice, and continuous ice cover rarely occurs. For example, chronicles have been preserved about how the Black Sea was covered with such strong ice in winter that merchants on sledges and on foot could reach the Turkish coast.
In general, the conditions of this water area are favorable for the development of flora and fauna. However, scientists have noticed that a decrease in salinity leads to a decrease in the biodiversity of the Black Sea. The fact is that the inhabitants of the World Ocean and its parts do not tolerate salinity below 20‰. For the population of Crimea, the desalination of low-salinity sea water in the water area near the Sea of Azov is a solution to the problem of drinking and technical water.
