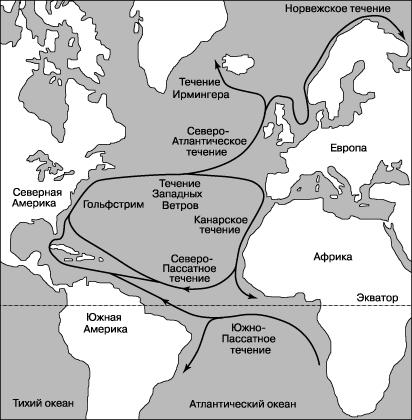
Many people know about the Gulf Stream, which, carrying huge masses of water from the equatorial latitudes to the polar ones, literally warms the north of Western Europe and Scandinavia. But few people know that there are other warm and cold currents of the Atlantic Ocean. How do they affect the climate of coastal areas? Our article will tell about it. In fact, there are a lot of currents in the Atlantic. We briefly list them for general development. These are the West Greenland, Angola, Antilles, Benguela, Guinea, Lomonosov, Brazilian, Guiana, Azores, Gulf Stream, Irminger, Canary, East Icelandic, Labrador, Portuguese, North Atlantic, Florida, Falkland, North Equatorial, South Equatorial, and also the Equatorial countercurrent . Not all of them have a big impact on the climate. Some of them are generally part or fragments of the main, larger currents. That's about them and will be discussed in our article.
Why do currents form?
In the World Ocean, large invisible "rivers without banks" are constantly circulating. Water in general is a very dynamic element. But everything is clear with rivers: they flow from the source to the mouth due to the difference in heights between these points. But what makes huge masses of water move within the ocean? Of the many reasons, two are the main ones: trade winds and changes in atmospheric pressure. Because of this, the currents are divided into drift and barogradient. The first are formed by trade winds - winds constantly blowing in one direction. Most of these currents Mighty rivers carry into the seas a large amount of water, different from sea water in density and temperature. Such currents are called stock, gravity and friction. Consideration should also be given to the great north-south extent of the Atlantic Ocean. The currents in this water area are therefore more meridional than latitudinal.
What are trade winds
Winds are the main reason for the movement of huge masses of water in the oceans. But what are the trade winds? The answer is to be found in the equatorial regions. The air warms up there more than in other latitudes. It rises and spreads along the upper layers of the troposphere towards the two poles. But already at a latitude of 30 degrees, having cooled thoroughly, it descends. Thus, a circulation of air masses is created. In the equatorial region, a zone of low pressure arises, and in tropical latitudes, a zone of high pressure. And here the rotation of the Earth around its axis manifests itself. If not for it, the trade winds would blow from the tropics of both hemispheres to the equator. But, as our planet rotates, the winds are deflected, becoming westerly. This is how the trade winds form the main currents of the Atlantic Ocean. In the Northern Hemisphere, they move clockwise, and in the Southern Hemisphere, they move counterclockwise. This is because in the first case, the trade winds blow from the northeast, and in the second - from the southeast.
Climate impact
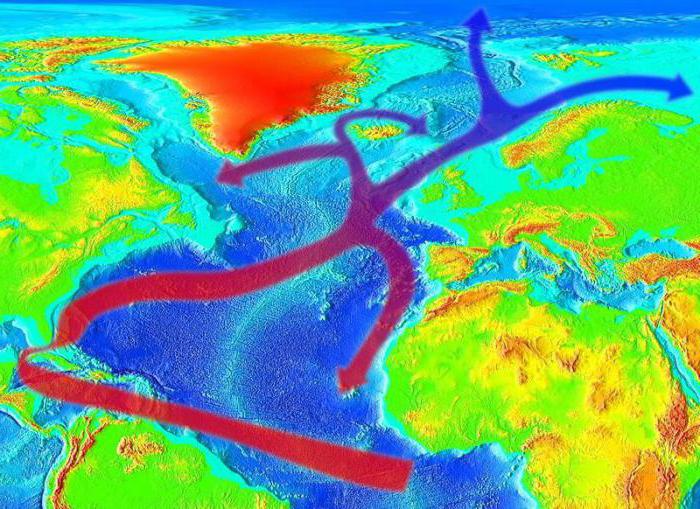
Based on the fact that the main currents originate in the equatorial and tropical regions, it would be reasonable to assume that they are all warm. But this does not always happen. The warm current in the Atlantic Ocean, having reached the polar latitudes, does not fade away, but, having made a smooth circle, reverses, but has already cooled down considerably. This can be seen in the example of the Gulf Stream. It carries warm masses of water from the Sargasso Sea to northern Europe. Then, under the influence of the rotation of the Earth, it deviates to the west. Under the name of the Labrador Current, it descends along the coast of the North American continent to the south, cooling the coastal regions of Canada. It should be said that these masses of water are conventionally called warm and cold - relative to the ambient temperature. For example, in the North Cape current in winter the temperature is only +2 °С, and in summer - maximum +8 °С. But it is called warm because the water in the Barents Sea is even colder.
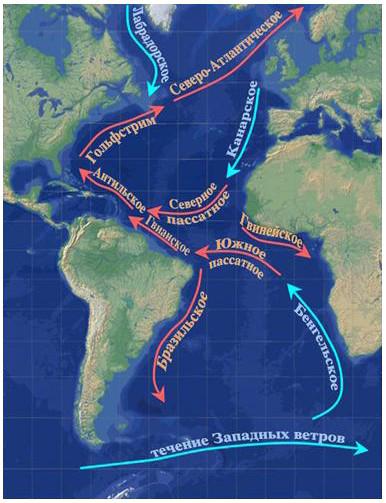
Major currents of the Atlantic in the Northern Hemisphere
Here, of course, one cannot fail to mention the Gulf Stream. But other currents passing through the Atlantic Ocean also have an important influence on the climate of nearby territories. Near Cape Verde (Africa), the northeast trade wind is born. It drives huge warm masses of water to the west. Crossing the Atlantic Ocean, they connect with the Antilles and Guiana currents. This enhanced jet moves towards the Caribbean Sea. After that, the waters rush to the north. This continuous clockwise movement is called the warm North Atlantic Current. Its edge at high latitudes is indefinite, blurred, and at the equator it is more distinct.
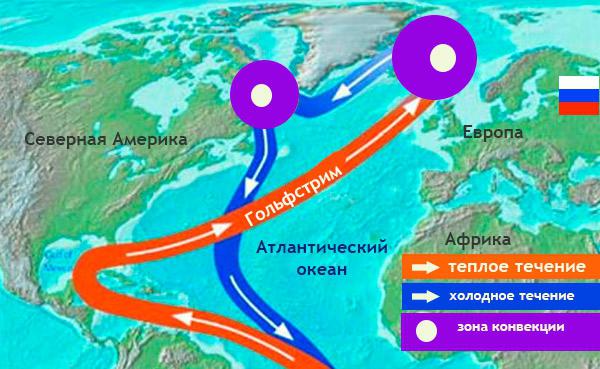
The mysterious "Current from the Gulf" (Golf-Stream)
This is the name of the course of the Atlantic Ocean, without which Scandinavia and Iceland would turn, based on their proximity to the pole, into the land of eternal snows. It used to be thought that the Gulf Stream was born in the Gulf of Mexico. Hence the name. In fact, only a small part of the Gulf Stream flows out of the Gulf of Mexico. The main flow comes from the Sargasso Sea. What is the mystery of the Gulf Stream? The fact that, contrary to the rotation of the Earth, it does not flow from west to east, but in the opposite direction. Its capacity exceeds the discharge of all the rivers of the planet. The speed of the Gulf Stream is impressive - two and a half meters per second on the surface. The current can be traced at a depth of 800 meters. And the width of the stream is 110-120 kilometers. Due to the high speed of the current, the water from the equatorial latitudes does not have time to cool. The surface layer has a temperature of +25 degrees, which, of course, plays a paramount role in shaping the climate of Western Europe. The mystery of the Gulf Stream is also that it does not wash the continents anywhere. There is always a strip of colder water between it and the shore.
Atlantic Ocean: Currents of the Southern Hemisphere
From the African continent to the American continent, the trade wind drives a jet, which, due to low pressure in the equatorial region, begins to deviate to the south. Thus begins a similar northern cycle. However, the South Equatorial Current moves counterclockwise. It also runs across the entire Atlantic Ocean. Currents Guiana, Brazilian (warm), Falkland, Benguela (cold) are part of this cycle.
