The importance of writing in the development of mankind is difficult to overestimate. Back in the era when the alphabet did not exist in sight, ancient people tried to express their thoughts in the form of rock inscriptions.
Alphabet of Elizabeth Boehm
First they drew figurines of animals and humans, then various signs and hieroglyphs. Over time, people managed to create easy-to-understand letters and put them into an alphabet. Who was the creator of the alphabet of the Russian language? To whom do we owe the opportunity to express ourselves freely through writing?
Who laid the foundation of the Russian alphabet?
The history of the emergence of the Russian alphabet goes back to the 2nd millennium BC. Then the ancient Phoenicians came up with consonants and used them for a long time to draw up documents.
In the VIII century BC, their discovery was borrowed by the ancient Greeks, who significantly improved the letter by adding vowels to it. In the future, it was the Greek alphabet, with the help of which statutory (solemn) letters were compiled, that formed the basis of the Russian alphabet.
Who created the Russian alphabet?
In the Bronze Age, Proto-Slavic peoples lived in Eastern Europe, speaking the same language. 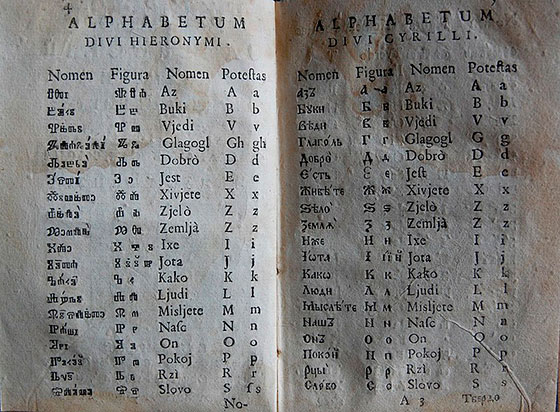 Primer Slavonic writings of the Greatest Teacher B. Jerome Stridon
Primer Slavonic writings of the Greatest Teacher B. Jerome Stridon
Around the 1st century AD, they began to break up into separate tribes, as a result of which several states inhabited by Eastern Slavs were created in these territories. Among them was Great Moravia, which occupied the lands of modern Czech Republic, Hungary, Slovakia, partly Ukraine and Poland.
With the advent of Christianity and the construction of temples, people needed to create a written language that would allow them to record church texts. To learn how to write, the Moravian prince Rostislav turned to the Byzantine emperor Michael III for help, who sent Christian preachers Cyril and Methodius to Moravia. In 863, they came up with the first Russian alphabet, which was named after one of the preachers - Cyrillic.
Who are Cyril and Methodius?
Cyril and Methodius were brothers from Thessalonica (now the Greek Thessaloniki). In those days, in their hometown, in addition to Greek, they spoke the Slavic-Thessalonica dialect, which formed the basis of the Church Slavonic language.
Initially, Cyril's name was Konstantin, and he received his second name just before his death, having taken a monastic vow. In his youth, Constantine studied with the best Byzantine teachers of philosophy, rhetoric, dialectics, and later taught at the University of Magnavra in Constantinople.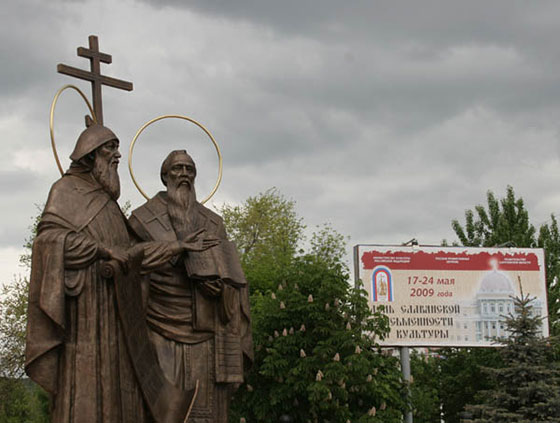  Monument to Saints Cyril and Methodius in Saratov. The author of the photo is Zimin Vasily.
Monument to Saints Cyril and Methodius in Saratov. The author of the photo is Zimin Vasily.
In 863, having gone to Moravia, with the help of his brother Methodius, he created. Bulgaria became the center for the dissemination of Slavic writing. In 886, the Preslav book school was opened on its territory, where they were engaged in translations from the Greek language and copied Cyrillic and Methodius originals. Around the same time, the Cyrillic alphabet came to Serbia, and at the end of the 10th century it reached Kievan Rus.
Initially, the first Russian alphabet had 43 letters. Later, 4 more were added to it, and the 14 former ones were removed as unnecessary. At first, some of the letters looked like Greek in appearance, but as a result of an orthographic reform in the 17th century, they were replaced by those that we know today.
By 1917, there were 35 letters in the Russian alphabet, although in fact there were 37 of them, since Yo and Y were not considered separate. Additionally, the letters I, Ѣ (yat), Ѳ (fita) and V (zhitsa) were present in the alphabet, which later disappeared from use.
When did the modern Russian alphabet appear?
In 1917-1918, a major spelling reform was carried out in Russia, thanks to which the modern alphabet appeared. Its initiator was the Ministry of Public Education under the Provisional Government. The reform began before the revolution, but was continued after the transfer of power to the Bolsheviks.  Wikimedia Commons / Jimmy Thomas ()
Wikimedia Commons / Jimmy Thomas ()
In December 1917, Russian statesman Anatoly Lunacharsky issued a decree requiring all organizations to use the new 33-letter alphabet.
Although the spelling reform was prepared before the revolution and had no political underpinnings, at first it was criticized by opponents of Bolshevism. However, over time, the modern alphabet took root and is used to this day.
