The Phoenicians, who kept constant trade records, needed a different letter - easy, simple and convenient. They came up with an alphabet in which each sign - a letter - denoted only one specific sound of speech.
The Phoenician alphabet consists of 22 simple letters. All of them are consonants, because consonants played the main role in the Phoenician language. To read a word, it was enough for a Phoenician to see its backbone, consisting of consonants.

The most ancient inscriptions, composed of the letters of the Phoenician alphabet, were found during excavations in the ancient city of Byblos (now the city of Jebel), at the foot of the Lebanese Range. They belong to the 13th century. BC. The Phoenicians wrote from right to left. They made their trade records in ink on potsherds. Few such shards have been found. The inscriptions carved on stone are better preserved: tombstones (on the sarcophagi of kings and priests) and building ones, telling about the construction of palaces at the behest of the Phoenician kings.
Starting from the IX century. BC e. The Phoenician alphabet began to spread rapidly in many countries. The Greek historian Herodotus wrote that the ancient Greeks learned writing from the Phoenicians. Indeed, even the names of the Greek letters themselves are Phoenician words. For example, the name of the letter "alpha" (A) comes from the Phoenician word "alef" - a bull. (The original form of this letter resembled a bull's head.) The name of the Greek letter "beta" comes from the Phoenician word "bet" - house. (Originally, this letter was a simplified drawing of a house plan.) The word "alphabet" itself is essentially a combination of the Phoenician words "alef" and "bet".
The letters in the Phoenician alphabet were arranged in a certain order. This order was also adopted by the Greeks. But in Greek, unlike Phoenician, vowels play an important role. At the same time, the Phoenician language had many guttural sounds alien to the Greeks. The Phoenician letters corresponding to these sounds were used by the Greeks to designate vowels. In addition, they came up with some new letters.
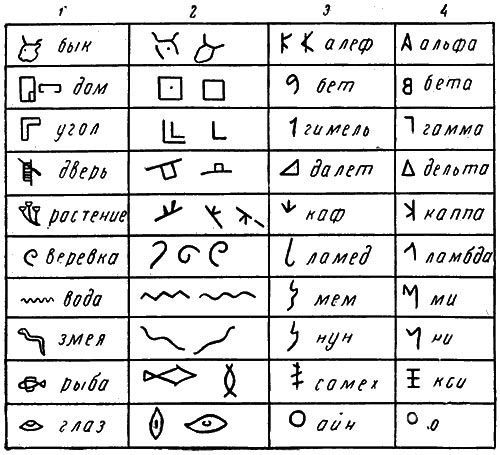
The Phoenician alphabet was incomparably simpler and more convenient than any cuneiform or hieroglyphs. But the Greek alphabet is even more perfect: it consists of 24 letters, denoting both vowels and consonants. The Greek alphabet formed the basis of the Latin, which, in turn, served as the basis for the alphabets of all Western European languages. The Church Slavonic alphabet originated from the Greek alphabet, compiled, according to legend, by the natives of the city of Thessaloniki (now the city of Thessaloniki) Cyril and Methodius. Under Peter I, the Church Slavonic alphabet was simplified, and an easier-to-read civil alphabet appeared, which we also use.
The Phoenician alphabet was the ancestor of not only the Greek, but also the Arabic, Hebrew and other alphabets. The invention of the Phoenicians was a great step in the cultural development of human society, making writing accessible to the masses.
